Home > Press > Building tailor-made DNA nanotubes step by step: New, block-by-block assembly method could pave way for applications in opto-electronics, drug delivery
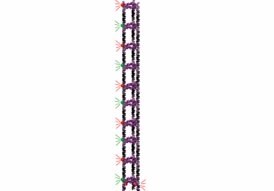 |
| In the new method for building nanotubes, blocks tagged with a fluorescent dye are incorporated step by step, enabling researchers to monitor formation of the structures as they are constructed. CREDIT: Graham D. Hamblin |
Abstract:
Researchers at McGill University have developed a new, low-cost method to build DNA nanotubes block by block - a breakthrough that could help pave the way for scaffolds made from DNA strands to be used in applications such as optical and electronic devices or smart drug-delivery systems.
Building tailor-made DNA nanotubes step by step: New, block-by-block assembly method could pave way for applications in opto-electronics, drug delivery
Montreal, Canada | Posted on February 23rd, 2015Many researchers, including the McGill team, have previously constructed nanotubes using a method that relies on spontaneous assembly of DNA in solution. The new technique, reported today in Nature Chemistry, promises to yield fewer structural flaws than the spontaneous-assembly method. The building-block approach also makes it possible to better control the size and patterns of the DNA structures, the scientists report.
"Just like a Tetris game, where we manipulate the game pieces with the aim of creating a horizontal line of several blocks, we can now build long nanotubes block by block," said Amani Hariri, a PhD student in McGill's Department of Chemistry and lead author of the study. "By using a fluorescence microscope we can further visualize the formation of the tubes at each stage of assembly, as each block is tagged with a fluorescent compound that serves as a beacon. We can then count the number of blocks incorporated in each tube as it is constructed."
This new technique was made possible by the development in recent years of single-molecule microscopy, which enables scientists to peer into the nano-world by turning the fluorescence of individual molecules on and off. (That groundbreaking work won three U.S.- and German-based scientists the 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.)
Hariri's research is jointly supervised by chemistry professors Gonzalo Cosa and Hanadi Sleiman, who co-authored the new study. Cosa's research group specializes in single-molecule fluorescence techniques, while Sleiman's uses DNA chemistry to design new materials for drug delivery and diagnostic tools.
The custom-built assembly technique developed through this collaboration "gives us the ability to monitor the nanotubes as we're building them, and see their structure, robustness and morphology," Cosa said.
"We wanted to control the nanotubes' lengths and features one-by-one," said Sleiman, who holds the Canada Research Chair in DNA Nanoscience. The resulting "designer nanotubes," she adds, promise to be far cheaper to produce on a large scale than those created with so-called DNA origami, another innovative technique for using DNA as a nanoscale construction material.
###
Funding for the research was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canada Foundation for Innovation, NanoQuébec, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fonds de recherché du Québec - Nature et technologies.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chris Chipello
514-398-4201
Copyright © McGill University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








