Home > Press > Half spheres for molecular circuits: Corannulene shows promising electronic properties
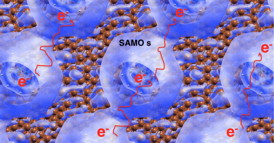 |
| This is a simulation of corannulene. CREDIT: SISSA/CNR IOM |
Abstract:
Imagine taking a fullerene (C60) and cutting it in half like a melon. What you get is a corannulene (C20H10), a molecule that, according to a just-published study conducted with SISSA's collaboration, could be an important component of future "molecular circuits", that is, circuits miniaturized to the size of molecules, to be used for various kinds of electronic devices (transistors, diodes, etc.).
Half spheres for molecular circuits: Corannulene shows promising electronic properties
Trieste, Italy | Posted on February 17th, 2015Fullerene is a very popular molecule: also called buckybowl, it is formed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal network shaped like a hollow sphere. It is an intensely studied material that displays interesting properties in different fields. Even though c60 is known to contain "empty states" (of a very special nature known as buckybowl superatom states, BSS) capable of accepting electrons, these states are found at very high energies, a feature that makes them difficult to exploit in electronic devices.
The electrons in electronic circuits have to be able to travel easily. "In fullerene the energy levels of the BSS type capable of accommodating 'travelling electrons' are difficult to achieve energetically", explains Layla Martin-Samos, researcher at Democritos IOM-CNR and SISSA and among the authors of the study published in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. "Corannullene, on the other hand, seems to be much better suited to the purpose, as demonstrated by our calculations".
Martin-Samos and colleagues had already studied the optical properties of this molecule. "This time instead we focused on its electronic properties with special emphasis on the study of BSS". The observations - theoretical and based on computer simulations - of Martin-Samos and colleagues show that BSS in corannulene are found at much lower energy levels compared to fullerene and can therefore be more easily accessed. "This makes the material an excellent prospective candidate for the construction of electronic circuits" continues Martin-Samos. "In fact if we put corannulene molecules next to one another in a row, the electrons will flow easily from one to the next, forming a sort of tunnel which makes up the circuit".
"Our work not only uncovered the potential of this molecule, but it also served as a guide for the subsequent experimental analysis, by indicating where and what to look at and reducing the time and cost of the experiments. The investigators have recently finished collecting the experimental data and are now going to start their analysis to verify experimentally what we observed in our simulation. We're keeping our fingers crossed: who knows, in a few months' time we might be celebrating".
###
Other study participants, in addition to SISSA and CNR-IOM, were the University of Zurich in Switzerland and the University of Nova Gorica in Slovenia.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Federica Sgorbissa
39-040-378-7644
Copyright © International School of Advanced Studies (SISSA)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Abstract of the original paper:
Abstract of the original paper:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








