Home > Press > Graphene enables all-electrical control of energy flow from light emitters: First signatures of graphene plasmons at telecommunications wavelength revealed
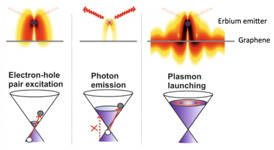 |
| This is an illustration of the electrically controlled energy flow into photons and plasmons. CREDIT: ICFO |
Abstract:
At the heart of lasers, displays and other light-emitting devices lies the emission of photons. Electrically controlled modulation of this emission is of great importance in applications such as optical communication, sensors and displays. Moreover, electrical control of the light emission pathways opens up the possibility of novel types of nano-photonics devices, based on active plasmonics.
Graphene enables all-electrical control of energy flow from light emitters: First signatures of graphene plasmons at telecommunications wavelength revealed
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on January 20th, 2015Scientists from ICFO, MIT, CNRS, CNISM and Graphenea have now demonstrated active, in-situ electrical control of the energy flow from erbium ions into photons and plasmons. The experiment was implemented by placing the erbium emitters a few tens of nanometers away from the graphene sheet, whose carrier density (Fermi energy) is electrically controlled. Partially funded by the EC Graphene Flagship, this study entitled "Electrical control of optical emitter relaxation pathways enabled by graphene", has been published in Nature Physics.
Erbium ions are essentially used for optical amplifiers and emit light at a wavelength of 1.5 micrometers, the so called third telecom window. This is an important window for optical telecommunications because there is very little energy loss in this range, and thus highly efficient information transmission.
The study has shown that the energy flow from erbium into photons or plasmons can be controlled simply by applying a small electrical voltage. The plasmons in graphene are rather unique, as they are very strongly confined, with a plasmon wavelength that is two orders of magnitude smaller than the wavelength of the emitted photons. As the Fermi energy of the graphene sheet was gradually increased, the erbium emitters went from exciting electrons in the graphene sheet, to emitting photons or plasmons. The experiments revealed the long-sought-after graphene plasmons at near-infrared frequencies, relevant for these telecommunications applications. In addition, the strong concentration of optical energy offers new possibilities for data storage and manipulation through active plasmonic networks.
Frank Koppens commented: "This work shows that electrical control of light at the nanometer scale is possible and efficient, thanks to the optoelectronics properties of graphene."
###
Funding Information
This work was funded by the E.C. under Graphene Flagship, as well as the NWO Rubicon fellowship, The Fundacio Cellex Barcelona, the ERC and the MIT MISTI-Spain program.
####
About ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences was created in 2002 by the government of Catalonia and the Technical University of Catalonia as a centre of research excellence devoted to the science and technologies of light with a triple mission: to conduct frontier research, train the next generation of scientists, and provide knowledge and technology transfer. Today, it is one of the top research centres worldwide in its category as measured by international rankings.
Research at ICFO targets the forefront of science and technology based on light with programs directed at applications in Health, Renewable Energies, Information Technologies, Security and Industrial processes, among others. The institute hosts 300 professionals based in a dedicated building situated in the Mediterranean Technology Park in the metropolitan area of Barcelona.
ICFO participates in a large number of projects and international networks of excellence and is host to the NEST program which is financed by Fundación Privada Cellex Barcelona. Ground-breaking research in graphene is being carried out at ICFO and through key collaborative research partnerships such as the FET Graphene Flagship. Prof Frank Koppens is the co-leader of the Optoelectonics work package within Flagship program.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alina Hirschmann
34-935-542-246
Copyright © ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








