Home > Press > Unraveling the light of fireflies
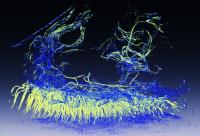 |
| This detailed microimage shows larger channels branching into smaller ones, supplying oxygen for the firefly's light emission. The smallest channels are ten thousand times smaller than a millimeter and therefore invisible to other experimental probes: this has prevented scientists so far to unlock the mystery of firefly light flashes.
Credit: Giorgio Margaritondo/EPFL |
Abstract:
Fireflies used rapid light flashes to communicate. This "bioluminescence" is an intriguing phenomenon that has many potential applications, from drug testing and monitoring water contamination, and even lighting up streets using glow-in-dark trees and plants. Fireflies emit light when a compound called luciferin breaks down. We know that this reaction needs oxygen, but what we don't know is how fireflies actually supply oxygen to their light-emitting cells. Using state-of-the-art imaging techniques, scientists from Switzerland and Taiwan have determined how fireflies control oxygen distribution to light up their cells. The work is published in Physical Review Letters.
Unraveling the light of fireflies
Lausanne, Switzerland | Posted on December 17th, 2014The firefly's light-producing organ is called the "lantern", and it is located in the insect's abdomen. It looks like a series of tubes progressing into smaller ones and so one, like a tree's branches growing into twigs. The function of these tubes, called, is to supply oxygen to the cells of the lantern, which contain luciferase and can produce light. However, the complexity of the firefly's lantern has made it difficult to study this mechanism in depth, and reproduce it for technological applications.
Giorgio Margaritondo at EPFL, Yeukuang Hwu at the Academia Sinica and their colleagues at the National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan have successfully used two sophisticated imaging techniques to overcome the complexity of the firefly lantern and map out how oxygen is supplied to light-emitting cells. The techniques are called synchrotron phase contrast microtomography and transmission x-ray microscopy. They can scan down to the level of a single cell, even allowing researchers to look inside it.
By applying these techniques on live fireflies, the scientists were able to see the entire structure of the lantern for the first time, and to also make quantitative evaluations of oxygen distribution.
The imaging showed that the firefly diverts oxygen from other cellular functions and puts it into the reaction that breaks up luciferin. Specifically, the researchers found that oxygen consumption in the cell decreased, slowing down energy production. At the same time, oxygen supply switched to light-emission.
The study is the first to ever show the firefly's lantern in such detail, while also providing clear evidence that it is optimized for light emission thanks to the state-of-the-art techniques used by the scientists. But Margaritondo points out another innovation: "The techniques we used have an advantage over, say, conventional x-ray techniques, which cannot easily distinguish between soft tissues. By using an approach based on changes in light intensity (phase-contrast) as opposed to light absorption (x-rays), we were able to achieve high-resolution imaging of the delicate firefly lantern."
###
This work represents a collaboration of EPFL with the following institutes in Taiwan: Academia Sinica, the National Tsing Hua University, the Endemic Species Research Institute, the National Taiwan University, and the National Cheng Kung University.
Reference
Tsai Y-L, Li C-W, Hong T-M, Ho J-Z, Yang E-C, Wu W-Y, Margaritondo G, Hsu S-T, Ong EBL, Hwu Y. Firefly Light Flashing: Oxygen Supply Mechanism. Physical Review Letters 17 December 2014.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nik Papageorgiou
41-216-932-105
Copyright © Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








