Home > Press > New technique allows low-cost creation of 3-D nanostructures
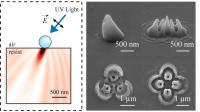 |
| Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new lithography technique that uses nanoscale spheres to create 3-D structures with biomedical, electronic and photonic applications. The nanospheres are transparent, but bend and scatter the light that passes through them in predictable ways according to the angle that the light takes when it hits the nanosphere. The researchers control the nanolithography by altering the size of the nanosphere, the duration of light exposures, and the angle, wavelength and polarization of light. The researchers can also use one beam of light, or multiple beams of light, allowing them to create a wide variety of nanostructure designs.
Credit: Xu Zhang, North Carolina State University |
Abstract:
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new lithography technique that uses nanoscale spheres to create three-dimensional (3-D) structures with biomedical, electronic and photonic applications. The new technique is significantly less expensive than conventional methods and does not rely on stacking two-dimensional (2-D) patterns to create 3-D structures.
New technique allows low-cost creation of 3-D nanostructures
Raleigh, NC | Posted on December 8th, 2014"Our approach reduces the cost of nanolithography to the point where it could be done in your garage," says Dr. Chih-Hao Chang, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State and senior author of a paper on the work.
Most conventional lithography uses a variety of techniques to focus light on a photosensitive film to create 2-D patterns. These techniques rely on specialized lenses, electron beams or lasers - all of which are extremely expensive. Other conventional techniques use mechanical probes, which are also costly. To create 3-D structures, the 2-D patterns are essentially printed on top of each other.
The NC State researchers took a different approach, placing nanoscale polystyrene spheres on the surface of the photosensitive film.
The nanospheres are transparent, but bend and scatter the light that passes through them in predictable ways according to the angle that the light takes when it hits the nanosphere. The researchers control the nanolithography by altering the size of the nanosphere, the duration of light exposures, and the angle, wavelength and polarization of light. The researchers can also use one beam of light, or multiple beams of light, allowing them to create a wide variety of nanostructure designs.
"We are using the nanosphere to shape the pattern of light, which gives us the ability to shape the resulting nanostructure in three dimensions without using the expensive equipment required by conventional techniques," Chang says. "And it allows us to create 3-D structures all at once, without having to make layer after layer of 2-D patterns."
The researchers have also shown that they can get the nanospheres to self-assemble in a regularly-spaced array, which in turn can be used to create a uniform pattern of 3-D nanostructures.
"This could be used to create an array of nanoneedles for use in drug delivery or other applications," says Xu Zhang, a Ph.D. student in Chang's lab and lead author of the paper.
The new technique could also be used to create nanoscale "inkjet printers" for printing electronics or biological cells, or to create antennas or photonic components.
"For this work, we focused on creating nanostructures using photosensitive polymers, which are commonly used in lithography," Zhang says. "But the technique could also be used to create templates for 3-D structures using other materials."
The researchers are currently looking at several additional ways to manipulate the technique to control the shape of resulting structures.
"We're exploring the use of nanosphere materials other than polystyrene, as well as nanoparticle shapes other than spheres," Chang says. "And ultimately we want to look at ways of controlling the placement of particles on the photosensitive film in patterns other than uniform arrays."
###
The paper, "Sculpting Asymmetric Hollow-Core Three-Dimensional Nanostructures Using Colloidal Particles," was published online Dec. 8 in the journal Small. The paper was co-authored by undergraduates Bin Dai and Zhiyuan Xu, who worked on the project at NC State as part of the Global Training Initiative (GTI) program with Jiangsu University. The work was supported by NASA Early Career Faculty grant number NNX12AQ46G and by the Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Advanced Self-Powered Systems of Integrated Sensors and Technologies at NC State under National Science Foundation grant number EEC-1160483.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








