Home > Press > New tool could help reshape the limits of synthetic biology: The 'telomerator' reshapes synthetic yeast chromosome into more flexible, realistic form, redefining what geneticists can build
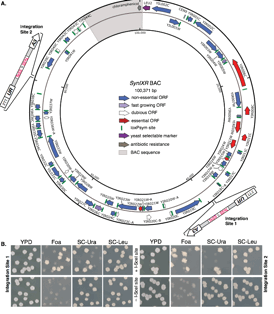 |
| A scientific schematic of the telomerator in action. Courtesy of PNAS |
Abstract:
NYU Langone yeast geneticists report they have developed a novel tool — dubbed "the telomerator" — that could redefine the limits of synthetic biology and advance how successfully living things can be engineered or constructed in the laboratory based on an organism's genetic, chemical base-pair structure.
New tool could help reshape the limits of synthetic biology: The 'telomerator' reshapes synthetic yeast chromosome into more flexible, realistic form, redefining what geneticists can build
New York, NY | Posted on November 3rd, 2014Synthetic biologists aim to use such "designer" microorganisms to produce novel medicines, nutrients, and biofuels.
In a report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences online Nov. 3, NYU Langone scientists say the telomerator should also improve study of yeast genetics, the model microorganism for human genetics, and help researchers determine how genes, as well as the chromosomes housing them, interact with each other.
The research team, led by Jef Boeke, PhD, a professor and director of NYU Langone's Institute for Systems Genetics, built the telomerator to convert circular chromosomes into linear ones. Boeke says this better resembles the natural structure of more complex organisms, including humans. Comprising about 1,500 chemical base pairs linked together, the man-made piece of telomerator code can be inserted as a single unit at any position on circular DNA and almost anywhere among a chromosome's other genes, whose base pairs can number into the hundreds of thousands.
"Our new telomerator resolves a serious and practical issue facing biologists everywhere by helping us experiment with synthetic genes in ways that are more realistic and more closely aligned to the biology of higher organisms, such as humans," says Boeke. "Until now, we've relied on synthesizing functional and stable yeast chromosomes in a circular format — with their telomeres cut off — so they can be uniformly reproduced for easy experimentation within bacteria, whose chromosomes are circular in shape," he says.
What makes the telomerator particularly effective, researchers say, is its precise capacity to add buffering chromosome endings, or telomeres, to newly linearized yeast chromosomes.
Moreover, the telomerator, which took Boeke and lead study investigator Leslie Mitchell, PhD, two years to construct and test, allows researchers to study how a gene's position or placement on a chromosome affects the gene's function.
The key components of the telomerator are its telomere seed sequences, which are exposed when the telomerator "cassette" — its packaged components — is activated.
To test the device, Mitchell inserted a telomerator cassette at 54 different locations on a circular synthetic yeast chromosome of about 90,000 base pairs and tested whether the chromosome could be segmented and straightened at each position. Researchers compared the process to a clock dial, in which they could insert the telomerator at any "hour" on the clock face to break the circle and yield 12 different timelines, but all of equal length. Colonies grew for 51 of the linear yeast chromosomes, failing only in chromosomes where essential genes were placed too close to the telomere ends.
Additional testing confirmed that the modified yeast chromosomes were in a linear format and of the precise length predicted by researchers.
Boeke's research is part of an international effort to manufacture all the yeast chromosomes, threadlike structures that carry genes in the nucleus of all plant and animal cells, and move genetic research one step closer to constructing the organism's entire functioning genome. Earlier this year, Boeke's team reported building the first of the 16 yeast chromosomes, which they call synIII, and successfully incorporating it into brewer's yeast, known scientifically as Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
###
Funding support for these latest experiments was provided by National Science Foundation grant MCB-0718846, Defense Advanced Research Project Agency contract N66001-12-C, and a postdoctoral fellowship grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
####
About NYU Langone Medical Center / New York University School of Medicine
NYU Langone Medical Center, a world-class, patient-centered, integrated academic medical center, is one of the nation's premier centers for excellence in clinical care, biomedical research, and medical education. Located in the heart of Manhattan, NYU Langone is composed of four hospitals — Tisch Hospital, its flagship acute care facility; Rusk Rehabilitation; the Hospital for Joint Diseases, the Medical Center's dedicated inpatient orthopaedic hospital; and Hassenfeld Children's Hospital, a comprehensive pediatric hospital supporting a full array of children's health services across the Medical Center — plus the NYU School of Medicine, which since 1841 has trained thousands of physicians and scientists who have helped to shape the course of medical history. The Medical Center's tri-fold mission to serve, teach, and discover is achieved 365 days a year through the seamless integration of a culture devoted to excellence in patient care, education, and research. For more information, go to www.NYULMC.org, and interact with us on Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David March
212-404-3528
Copyright © New York University School of Medicine
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Synthetic Biology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








