Home > Press > Engineered proteins stick like glue — even in water: New adhesives based on mussel proteins could be useful for naval or medical applications
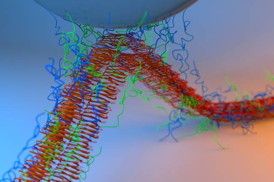 |
| This image shows adhesion between the silica tip of an atomic force microscope and adhesive fibers made by fusing mussel foot proteins and curli amyloid fibers.
Image: Yan Liang |
Abstract:
Shellfish such as mussels and barnacles secrete very sticky proteins that help them cling to rocks or ship hulls, even underwater. Inspired by these natural adhesives, a team of MIT engineers has designed new materials that could be used to repair ships or help heal wounds and surgical incisions.
Engineered proteins stick like glue — even in water: New adhesives based on mussel proteins could be useful for naval or medical applications
Cambridge, MA | Posted on September 22nd, 2014To create their new waterproof adhesives, the MIT researchers engineered bacteria to produce a hybrid material that incorporates naturally sticky mussel proteins as well as a bacterial protein found in biofilms — slimy layers formed by bacteria growing on a surface. When combined, these proteins form even stronger underwater adhesives than those secreted by mussels.
This project, described in the Sept. 21 issue of the journal Nature Nanotechnology, represents a new type of approach that can be exploited to synthesize biological materials with multiple components, using bacteria as tiny factories.
"The ultimate goal for us is to set up a platform where we can start building materials that combine multiple different functional domains together and to see if that gives us better materials performance," says Timothy Lu, an associate professor of biological engineering and electrical engineering and computer science (EECS) and the senior author of the paper.
The paper's lead author is Chao Zhong, a former MIT postdoc who is now at ShanghaiTech University. Other authors are graduate student Thomas Gurry, graduate student Allen Cheng, senior Jordan Downey, postdoc Zhengtao Deng, and Collin Stultz, a professor in EECS.
Complex adhesives
The sticky substance that helps mussels attach to underwater surfaces is made of several proteins known as mussel foot proteins. "A lot of underwater organisms need to be able to stick to things, so they make all sorts of different types of adhesives that you might be able to borrow from," Lu says.
Scientists have previously engineered E. coli bacteria to produce individual mussel foot proteins, but these materials do not capture the complexity of the natural adhesives, Lu says. In the new study, the MIT team wanted to engineer bacteria to produce two different foot proteins, combined with bacterial proteins called curli fibers — fibrous proteins that can clump together and assemble themselves into much larger and more complex meshes.
Lu's team engineered bacteria so they would produce proteins consisting of curli fibers bonded to either mussel foot protein 3 or mussel foot protein 5. After purifying these proteins from the bacteria, the researchers let them incubate and form dense, fibrous meshes. The resulting material has a regular yet flexible structure that binds strongly to both dry and wet surfaces.
"The result is a powerful wet adhesive with independently functioning adsorptive and cohesive moieties," says Herbert Waite, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of California at Santa Barbara who was not part of the research team. "The work is very creative, rigorous, and thorough."
The researchers tested the adhesives using atomic force microscopy, a technique that probes the surface of a sample with a tiny tip. They found that the adhesives bound strongly to tips made of three different materials — silica, gold, and polystyrene. Adhesives assembled from equal amounts of mussel foot protein 3 and mussel foot protein 5 formed stronger adhesives than those with a different ratio, or only one of the two proteins on their own.
These adhesives were also stronger than naturally occurring mussel adhesives, and they are the strongest biologically inspired, protein-based underwater adhesives reported to date, the researchers say.
More adhesive strength
Using this technique, the researchers can produce only small amounts of the adhesive, so they are now trying to improve the process and generate larger quantities. They also plan to experiment with adding some of the other mussel foot proteins. "We're trying to figure out if by adding other mussel foot proteins, we can increase the adhesive strength even more and improve the material's robustness," Lu says.
The team also plans to try to create "living glues" consisting of films of bacteria that could sense damage to a surface and then repair it by secreting an adhesive.
The research was funded by the Office of Naval Research, the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Marine/Watercraft
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








