Home > Press > Researchers Create World’s Largest DNA Origami
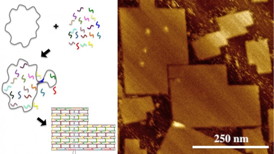 |
| Scaffolded DNA origami utilizes numerous chemically synthesized, short DNA strands (staple strands) to direct the folding of a larger, biologically derived strand of DNA (scaffold strand). Molecular recognition (base pairing, i.e., A binds to T and G binds to C) directs the DNA to self-assemble into a specific structure as programed by the staple strand sequences. Unique staple strands produce a molecular pegboard with single-digit nanometer site-specificity precision. The atomic force microscopy image (right) demonstrates the final origami structure. Image credit: Alexandria Marchi. |
Abstract:
"Toward Larger DNA Origami"
Authors: Alexandria N. Marchi and Ishtiaq Saaem, Duke University; Briana N. Vogen and Thomas H. LaBean, North Carolina State University; Stanley Brown, University of Copenhagen
Published: online Sept. 1, Nano Letters
DOI: 10.1021/nl502626s
Abstract: Structural DNA nanotechnology, and specifically scaffolded DNA origami, is rapidly developing as a versatile method for bottom-up fabrication of novel nanometer-scale materials and devices. However, lengths of conventional single-stranded scaffolds, for example, 7,249-nucleotide circular genomic DNA from the M13mp18 phage, limit the scales of these uniquely addressable structures. Additionally, increasing DNA origami size generates the cost burden of increased staple-strand synthesis. We addressed this 2-fold problem by developing the following methods: (1) production of the largest to-date biologically derived single-stranded scaffold using a λ/M13 hybrid virus to produce a 51 466-nucleotide DNA in a circular, single-stranded form and (2) inexpensive DNA synthesis via an inkjet-printing process on a chip embossed with functionalized micropillars made from cyclic olefin copolymer. We have experimentally demonstrated very efficient assembly of a 51-kilobasepair origami from the λ/M13 hybrid scaffold folded by chip-derived staple strands. In addition, we have demonstrated two-dimensional, asymmetric origami sheets with controlled global curvature such that they land on a substrate in predictable orientations that have been verified by atomic force microscopy.
Researchers Create World’s Largest DNA Origami
Raleigh, NC | Posted on September 11th, 2014Researchers from North Carolina State University, Duke University and the University of Copenhagen have created the world's largest DNA origami, which are nanoscale constructions with applications ranging from biomedical research to nanoelectronics.
"These origami can be customized for use in everything from studying cell behavior to creating templates for the nanofabrication of electronic components," says Dr. Thom LaBean, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and senior author of a paper describing the work.
DNA origami are self-assembling biochemical structures that are made up of two types of DNA. To make DNA origami, researchers begin with a biologically derived strand of DNA called the scaffold strand. The researchers then design customized synthetic strands of DNA, called staple strands. Each staple strand is made up of a specific sequence of bases (adenine, cytosine, thaline and guanine - the building blocks of DNA), which is designed to pair with specific subsequences on the scaffold strand.
The staple strands are introduced into a solution containing the scaffold strand, and the solution is then heated and cooled. During this process, each staple strand attaches to specific sections of the scaffold strand, pulling those sections together and folding the scaffold strand into a specific shape.
The standard for DNA origami has long been limited to a scaffold strand that is made up of 7,249 bases, creating structures that measure roughly 70 nanometers (nm) by 90 nm, though the shapes may vary.
However, the research team led by LaBean has now created DNA origami consisting of 51,466 bases, measuring approximately 200 nm by 300 nm.
"We had to do two things to make this viable," says Dr. Alexandria Marchi, lead author of the paper and a postdoctoral researcher at Duke. "First we had to develop a custom scaffold strand that contained 51 kilobases. We did that with the help of molecular biologist Stanley Brown at the University of Copenhagen.
"Second, in order to make this economically feasible, we had to find a cost-effective way of synthesizing staple strands - because we went from needing 220 staple strands to needing more than 1,600," Marchi says.
The researchers did this by using what is essentially a converted inkjet printer to synthesize DNA directly onto a plastic chip.
"The technique we used not only creates large DNA origami, but has a fairly uniform output," LaBean says. "More than 90 percent of the origami are self-assembling properly."
The paper, "Toward Larger DNA Origami," is published online in Nano Letters. The paper was co-authored by Dr. Ishtiaq Saaem, a former Ph.D. student at Duke; Dr. Briana Vogen, a former postdoctoral researcher at NC State; and Dr. Stanley Brown at the University of Copenhagen.
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation under grants CDI-0835794, OISE-1246799, and EPMD-1231888, and by the University of Copenhagen.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Dr. Thomas LaBean
919.515.2204
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








