Home > Press > Promising Ferroelectric Materials Suffer From Unexpected Electric Polarizations: Brookhaven Lab scientists find surprising locked charge polarizations that impede performance in next-gen materials that could otherwise revolutionize data-driven devices
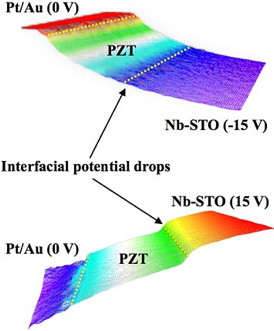 |
| Electrostatic potential landscapes reconstructed from electron holography data with 15 volts of positive or negative current applied to the substrate (Nb-STO). The much steeper potential drop from the +15 V signifies a higher electric field, whereas the -15 V yielded a much flatter curve—indicating the charge asymmetry within the material. |
Abstract:
Electronic devices with unprecedented efficiency and data storage may someday run on ferroelectrics—remarkable materials that use built-in electric polarizations to read and write digital information, outperforming the magnets inside most popular data-driven technology. But ferroelectrics must first overcome a few key stumbling blocks, including a curious habit of "forgetting" stored data.
Promising Ferroelectric Materials Suffer From Unexpected Electric Polarizations: Brookhaven Lab scientists find surprising locked charge polarizations that impede performance in next-gen materials that could otherwise revolutionize data-driven devices
Upton, NY | Posted on August 18th, 2014Now, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered nanoscale asymmetries and charge preferences hidden within ferroelectrics that may explain their operational limits.
"The positive or negative polarizations in these ferroelectric materials should be incredibly easy to switch, but the reality is much stranger," said Brookhaven Lab physicist Myung-Geun Han, lead author on the new study. "To our surprise, opposing electronic configurations only allowed for polarization in one direction—a non-starter for reading and writing data."
The researchers used a suite of state-of-the-art techniques—including real-time electrical biasing, electron holography, and electron-beam-induced current measurements—to reveal never-before-seen electric field distributions in ferroelectric thin films, which were custom-grown at Yale University. The results, published in Nature Communications, open new pathways for ferroelectric technology.
Physics of Flipping
Most electronic devices rely on ferromagnetism to read and write data. Each so-called ferromagnetic domain contains a north or south magnetic polarity, which translates into the flipping 1 or 0 of the binary code underlying all digital information. But ferromagnetic operations not only require large electric current, but the magnets can flip each other like dominoes when packed together too tightly—effectively erasing any data.
Ferroelectrics, however, use positive or negative electric charge to render digital code. Crucially, they can be packed together with domains spanning just a few atoms and require only a tiny voltage kick to flip the charge, storing much more information with much greater efficiency.
"But ferroelectric commercialization is held up by material fatigue, sudden polarization reversal, and intrinsic charge preferences," said Brookhaven Lab physicist and study coauthor Yimei Zhu. "We suspected that the origin of these issues was in the atomic interactions along the material's interface—where the ferroelectric thin film sits on a substrate."
Interface Exploration
The scientists examined ferroelectric films of lead, zirconium, and titanium oxide grown on conductive substrates of strontium, and titanium oxide with a small amount of niobium—chosen because it exhibits large polarization values with well-defined directions, either up or down. The challenge was mapping the internal electric fields in materials thousands of times thinner than a human hair under actual operating conditions.
Brookhaven scientists hunted down the suspected interface quirks using electron holography. In this technique, a transmission electron microscope (TEM) fired 200,000-volt electron wave packets through the sample with billionth-of-a-meter precision. Negative and positive electric fields inside the ferroelectric film then attracted or repelled the electron wave and slightly changed its direction. Tracking the way the beam bent throughout the ferroelectric film revealed its hidden charges.
"Rather than an evenly distributed electric field, the bending electron waves revealed non-uniform and unidirectional electric fields that induced unstable, head-to-head domain configurations," Han said. "For the first time, we could see these unusual and jagged polarizations mapped out in real space and real time."
These opposing polarizations—like rival football teams squaring off aggressively at the line of scrimmage—surprised scientists and challenged assumptions about the ferroelectric phenomenon.
"These results were totally unexpected based on the present understanding of ferroelectrics," Han said.
The asymmetries were further confirmed by measurements of electron-beam-induced current. When a focused electron beam struck the ferroelectric sample, electric fields within the film-substrate interface revealed themselves by generating additional current. Other techniques, including piezoresponse force microscopy—in which a sub-nanometer tip induces a reaction by pressing against the ferroelectric—also confirmed the strange domains.
"Each technique demonstrated this intrinsic polarization preference, likely the origin of the back-switching and poor coding performance in these ferroelectrics," Han said. "But these domain structures should require a lot of energy and thus be very unstable. The interface effect alone cannot explain their existence."
Missing Oxygen
The scientists used another ultra-precise technique to probe the material's interface: electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). By measuring the energy deposited by an electron beam in specific locations—a kind of electronic fingerprint—the scientists determined the material's chemical composition.
"We suspect that more oxygen could be missing near the surface of the thin films, creating electron pockets that may neutralize positive charges at the domain walls," Han said. "This oxygen deficiency naturally forms in the material, and it could explain the stabilization of head-to-head domains."
This electron-swapping oxygen deficiency—and its negative effects on reliably storing data—might be corrected by additional engineering, Han said. For example, incorporating a "sacrificial layer" between the ferroelectric and the substrate could help block the interface interactions. In fact, the study may inspire new ferroelectrics that either exploit or overcome this unexpected charge phenomenon.
Other authors include Lijun Wu and Marvin A. Schofield of Brookhaven Lab; Matthew S. J. Marshall, Jason Hoffman, Frederick J. Walker, and Charles H. Ahn of the Yale University Department of Applied Physics and Center for Research on Interfaces Structures and Phenomena; Toshihiro Aoki of JEOL USA Inc.; and Ray Twesten of Gatan Inc.
The samples used for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were prepared by Kim Kisslinger at Brookhaven Lab's Center for Functional Nanomaterials, a U.S. Department of Energy user facility.
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation for the State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit applied science and technology organization.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Justin Eure
631-344-2347
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








