Home > Press > Optimum inertial design for self-propulsion: A new study investigates the effects of small but finite inertia on the propulsion of micro and nano-scale swimming machines
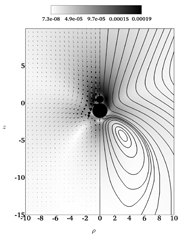 |
| Streamlines, velocity field, and magnitude of the share of the propelling flow attributed to the low level inertial force, in the case of touching spheres | © Nadal et al. |
Abstract:
Scale plays a major role in locomotion. Swimming microorganisms, such as bacteria and spermatozoa, are subjected to relatively small inertial forces compared to the viscous forces exerted by the surrounding fluid. Such low-level inertia makes self-propulsion a major challenge. Now, scientists have found that the direction of propulsion made possible by such inertia is opposite to that induced by a viscoelastic fluid. These findings have been published in EPJ E by François Nadal from the Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), in Le Barp, France, and colleagues. This study could help to optimise the design of self-propelled micro- and nanoscale artificial swimming machines to improve their mobility in medical applications.
Optimum inertial design for self-propulsion: A new study investigates the effects of small but finite inertia on the propulsion of micro and nano-scale swimming machines
Heidelberg, Germany and New York, NY | Posted on July 29th, 2014The authors focus on two joined spheres of different radii—dubbed a dumbbell—rotating in a model fluid. They first use simulation to study the effect of a small-scale inertial force on the dumbbell's propulsion. They then compare it with results from theoretical calculations describing locomotion.
They demonstrate that despite the geometrical asymmetry, such a dumbbell cannot self-propel in a pure Newtonian fluid—which is a model fluid whose viscosity does not change with its flow rate—in the absence of inertia. This is because of the underlying laws of physics. If a dumbbell rotating in the counter-clockwise direction propels upwards in the absence of inertia, it would have to move downwards when rotating in the counter-clockwise direction. As both problems are mirror-image symmetric from each other, their propulsion should occur in the same direction and thus without inertia a rotating dumbbell cannot self-propel.
Furthermore, the study shows that a rotating dumbbell propels with the large sphere due to inertial forces in the fluid and the small sphere ahead in a pure viscoelastic fluid. With this in mind, the authors then derive the optimal dumbbell geometry for a self-propelling small-scale swimmer.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Zimmermann
49-622-148-78414
Copyright © Springer
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








