Home > Press > Interlayer distance in graphite oxide gradually changes when water is added
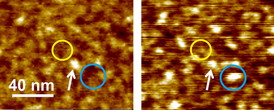 |
| Scanning force microscopy images, which show the relief of a graphene oxide flake. Bright areas are "hills" and dark areas are "valleys". The left image was recorded at low relative humidity, one can say on a dry surface. The right image was recorded at high relative humidity, 65 percent. One can see that new bright spots appear in some regions, which are due to the insertion of water. The overall relief becomes less flat and more curved with more hills while valleys are preserved. |
Abstract:
Physicists from Umeć University and Humboldt University in Berlin have solved a mystery that has puzzled scientists for half a century. They show with the help of powerful microscopes that the distance between graphite oxide layers gradually increases when water molecules are added. That is because the surface of graphite oxide is not flat, but varies in thickness with "hills" and "valleys" of nanosize. The new findings are published in the scientific journal Nano Letters.
Interlayer distance in graphite oxide gradually changes when water is added
Umea, Sweden | Posted on June 30th, 2014"Now we can better understand the mechanisms of solvent insertion between layers of graphene oxide. It increases our knowledge of the ultrathin membranes and helps to design new types of membranes with permeation properties that can be finely adjusted by adding water and various other solvents,"says Alexandr Talyzin, researcher at the Department of Physics at Umeć University.
Graphite oxide is a unique and useful material, with many unusual properties. It can easily dissolve in water and form single atomic layers of graphene oxide sheets. The super thin flakes can then be arranged in a multilayer membrane with the unique ability to incorporate various solvents between the layers.
Already in the 60's such membranes were tested for seawater desalination and filtration applications. Recent studies show that the graphene oxide membranes may also be used to separate liquids and gases. Thin graphene oxide films can separate binary gas mixtures with fairly high efficiency. Even more interesting, the separation characteristics can be finely adjusted by water vapors.
Water molecules easily penetrate between the graphene oxide layers and it has long been known that the distance between the graphene oxide layers depends on the humidity. By simple logic, it means that the distance between the layers is to change in steps corresponding to the size of the water molecules. What has puzzled scientists for half a century is that the distance between the layers, as measured by diffraction methods, is gradually changing proportionally to the humidity change.
"Obviously, we cannot put in quarter molecules or half molecules. So why do we see continuous changes in the distance between the graphene oxide layers? We decided to study the layers of graphene oxide with modern microscopic methods, which strangely enough had not been done before", says Alexandr Talyzin.
So far the puzzle had been explained with a phenomenon called interstratification - a random stacking of layers with different number of water layers - and what is measured by diffraction data has been an average value related to the different proportions between the number of layers having different degrees of hydration.
The new study conducted by physicists from Humboldt University in Berlin together with Alexandr TalyzinŽs research team at Umeć University provides a different explanation. With microscopy of very high resolution, Scanning Force Microscopy, the researchers could measure the absolute distance between two graphene oxide layer and record changes as a function of humidity.
"The distance between two single graphene oxide layers obviously changed gradually again, but the explanation for this effect was revealed as nanometer-sized areas that were not equally filled with water. Of course, the effect of interstratification was excluded in our experiments because we only studied two layers and a single distance", says Alexandr Talyzin.
The results indicate that picturing graphene oxide as a flat plane is not correct. It is, rather, a relatively thick layer (about two times the thickness of graphene) with a variation of thickness, including "hills" and "valleys" of different size. Adding water molecules increases the thickness of this layer locally, but not necessary by the exact size of the water molecule if some "valleys" are filled first. When all available water adsorption sites ("valleys") are filled, an additional water layer is added at once. This happens at very high humidity or in liquid water.
About graphite oxide:
Graphene is a thin film of carbon, only one atom thick. It is a unique adsorptive material because of its extremely large surface. One gram graphene has a surface comparable to a football field. This space would be ideal for adsorption of gases and liquids in applications for gas storage, extraction of impurities from water, and so on, unless the graphene would be hydrophobic, meaning that its surface repels water. Oxidation of graphene results in notable changes of its properties. Graphene oxide is hydrophilic and attracted to water, and is even highly soluble in water. A material consisting of many graphene oxide layers is called graphite oxide. One possible application in the environmental area is purifying contaminated soil and seawater. Graphene oxide functions as a filter that separates all other components in water, except the water molecules.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alexandr Talyzin
46-907-866-320
Copyright © Umea University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








