Home > Press > Nanoscale velcro used for molecule transport
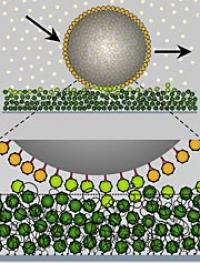 |
| This image shows an import protein coated molecule moving on the "dirty velcro."
Credit: Biozentrum, University of Basel |
Abstract:
Biological membranes are like a guarded border. They separate the cell from the environment and at the same time control the import and export of molecules. The nuclear membrane can be crossed via many tiny pores. Scientists at the Biozentrum and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel, together with an international team of researchers, have discovered that proteins found within the nuclear pore function similar to a velcro. In Nature Nanotechnology, they report how these proteins can be used for controlled and selective transport of particles.
Nanoscale velcro used for molecule transport
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on June 25th, 2014There is much traffic in our cells. Many proteins, for example, need to travel from their production site in the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where they are used to read genetic information. Pores in the nuclear membrane enable their transport into and out of the cell nucleus. The Argovia Professor Roderick Lim, from the Biozentrum and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel, studies the biophysical basics of this transport. In order to better understand this process, he has created an artificial model of the nuclear pore complex, together with scientists from Lausanne and Cambridge, which has led to the discovery that its proteins function like a nanoscale "velcro" which can be used to transport tiniest particles.
"Dirty velcro" inside the nuclear pore
Nuclear pores are protein complexes within the nuclear membrane that enables molecular exchange between the cytoplasm and nucleus. The driving force is diffusion. Nuclear pores are lined with "velcro" like proteins. Only molecules specially marked with import proteins can bind to these proteins and thus pass the pore. But for all non-binding molecules the nuclear pore acts as a barrier. The researchers postulated that transport depends on the strength of binding to the "velcro" like proteins. The binding should be just strong enough that molecules to be transported can bind but at the same time not too tight so that they can still diffuse through the pore.
In an artificial system recreating the nuclear pore, the researchers tested their hypothesis. They coated particles with import proteins and studied their behavior on the molecular "velcro". Interestingly, the researchers found parallels in behavior to the velcro strip as we know it. On "clean velcro", the particles stick immediately. However, when the "velcro" is filled or "dirtied" with import proteins, it is less adhesive and the particles begin to slide over its surface just by diffusion. "Understanding how the transport process functions in the nuclear pore complex was decisive for our discovery," says Lim. "With the nanoscale 'velcro' we should be able to define the path to be taken as well as speed up the transport of selected particles without requiring external energy."
Potential lab-on-a-chip technology applications
Lim's investigations of biomolecular transport processes form the basis for the discovery of this remarkable phenomenon that particles can be transported selectively with a molecular "velcro". "This principle could find very practical applications, for instance as nanoscale conveyor belts, escalators or tracks," explains Lim. This could also potentially be applied to further miniaturize lab-on-chip technology, tiny labs on chips, where this newly discovered method of transportation would make today's complex pump and valve systems obsolete.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Katrin Bühler
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








