Home > Press > Short nanotubes target pancreatic cancer: Rice, MD Anderson scientists refine technique for attacking hard-to-reach tumors - See more at: http://news.rice.edu/2014/06/05/short-nanotubes-target-pancreatic-cancer/#sthash.If4knT1G.dpuf
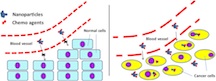 |
| Rice researchers found that chemotherapy agents attached to nanotubes are too large to go through the pores of normal blood vessels (left), but small enough to pass through the pores of cancer-related vessels. Once through, the customized nanotubes can be taken up by cancer cells to deliver their therapeutic cargoes. Credit: Rei Suzuki/University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center |
Abstract:
Short, customized carbon nanotubes have the potential to deliver drugs to pancreatic cancer cells and destroy them from within, according to researchers at Rice University and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Short nanotubes target pancreatic cancer: Rice, MD Anderson scientists refine technique for attacking hard-to-reach tumors - See more at: http://news.rice.edu/2014/06/05/short-nanotubes-target-pancreatic-cancer/#sthash.If4knT1G.dpuf
Houston, TX | Posted on June 5th, 2014Pristine nanotubes produced through a new process developed at Rice can be modified to carry drugs to tumors through gaps in blood-vessel walls that larger particles cannot fit through.
The nanotubes may then target and infiltrate the cancerous cells' nuclei, where the drugs can be released through sonication - that is, by shaking them.
The research led by Rice chemist Andrew Barron was reported in the Royal Society of Chemistry's Journal of Materials Chemistry B.
Most pancreatic cancer patients die within a year of diagnosis and have a five-year survival rate of 6 percent, partially because there is no method for early detection, according to the American Cancer Society. Tumors are often inoperable and pancreatic cancer cells are also difficult to reach with chemotherapy, said co-author Jason Fleming, a professor of surgical oncology at MD Anderson.
"These findings are encouraging because they offer a potential delivery solution for pancreatic cancer patients whose tumors resist standard chemotherapy," Fleming said. "There are molecular and biological barriers to efficient delivery of chemotherapy to pancreatic cancer tumors, and these nanotubes might be able to make some of those irrelevant."
Rice scientists made nanotubes pure enough to modify for the purpose and small enough to squeeze through the body's defenses, Barron said. The researchers knew from previous work that nanotubes could be modified - a process called functionalization - to carry chemotherapy agents and release them at a controlled rate through sonication.
"This time, we were trying to work out how long the tubes should be and the extent of functionalization to maximize uptake by the cells," Barron said.
Several discoveries were key, he said. First, Rice graduate student, alumnus and co-author Alvin Orbaek purified the carbon nanotubes of iron catalysts necessary to their growth by flushing them with chlorine. "Leftover iron particles damage the tubes through oxidation," Barron said. "That makes subsequent use difficult."
The next step was to cut the nanotubes down to size. Very long nanotubes are floppy and hard to deal with, Barron said. Enrico Andreoli, a postdoctoral research associate in Barron's group and lead author of the paper, used a thermal process to chop them to an average length of 50 nanometers. (A human hair is about 100,000 nanometers wide.)
"Instead of ending up with a fluffy nanotube powder, we get something that looks like a hockey puck," Barron said. "It's not dense - it looks like a spongy puck - but you can cut it with a razor blade. You can weigh it and do accurate chemistry with it."
Barron's lab added polyethyleneimine (PEI) to the nanotube surfaces. In lab tests, the modified tubes were easily dispersed in liquid and able to pass through barriers into live cancer cells to infiltrate the nuclei. A small-molecule variant of PEI proved to be less toxic to cells than larger versions, Barron said.
"This research shows that the particles are small enough to get inside cells where you like them to be and that they may have an increased killing advantage - but that's still unknown," Fleming said.
Fleming, whose work focuses on improving drug delivery for pancreatic cancer, cautioned that more research is required. "The next step will be to test this approach in mice that have allografts taken from human tumors," he said. "The architecture of these tumors will more closely resemble that of human pancreatic cancer."
Co-authors are Robert Hauge, a distinguished faculty fellow in chemistry, and Wade Adams, a senior faculty fellow in materials science and nanoengineering, both at Rice, and postdoctoral fellow Rei Suzuki and Manoop Bhutani, a professor of gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition, both at MD Anderson. Barron is Rice's Charles W. Duncan Jr.-Welch Professor of Chemistry and a professor of materials science and nanoengineering.
The Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders, the National Institutes of Health through MD Anderson's Cancer Center Support Grant and the Robert A. Welch Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for “best value” among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center:
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








