Home > Press > Nanoshell-emitters hybrid nanoobject was proposed as promising 2-photon fluorescence probe
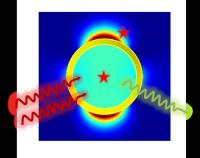 |
| This is a schematic presentation of plasmonic-enhanced two-photon fluorescence of a single emitter inside or outside of an individual gold nanoshell.
Credit: ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Two-photon excitation fluorescence is growing in popularity in the bioimaging field but is limited by fluorophores' extremely low two-photon absorption cross-section. The researcher Dr. Guowei Lu and co-workers from State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Department of Physics, Peking University, are endeavoring to develop efficient fluorescent probes with improved two-photon fluorescence (TPF) performance. They theoretically present a promising bright probe using gold nanoshell to improve the TPF performances of fluorescent emitters. Their work, entitled "Plasmonic-Enhanced Two-Photon Fluorescence with Single Gold Nanoshell", was published in SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy.2014, Vol 57(6).
Nanoshell-emitters hybrid nanoobject was proposed as promising 2-photon fluorescence probe
Shenyang, PR China | Posted on May 22nd, 2014The strategy of using metallic nanoparticles to achieve the TPF enhancement is an appealing scheme so-called metal-enhanced fluorescence. It is based on the coupling of the fluorophores and the plasmonic nanoparticles, resulting in enhanced fluorescence intensity, shortened fluorescence lifetime, and extended photostability. Specifically, the fluorescence enhancement can be optimally controlled through simultaneous efficient coupling between the excitation and emission processes of emitters and the dipolar and quadrupolar modes of the nanoparticles, respectively.
Among various types of metal nanoparticles, metallic nanoshells are especially suitable as the carriers of fluorescent emitters to construct hybrid TPF probes, because their plasmon resonance bands easily span the near-infrared region where biological tissues display minimal autofluorescence and absorption. The nanoshells act as optical antenna enabling the local field enhancement, the increase in radiative decay rate of the fluorophore that alters the quantum efficiency, and modulation of the far-field radiative coupling of fluorescence emission through nanoparticle scattering. Also, the core shell structure offers a perfect platform for designing and fabricating multifunctional nanoparticles.
The Peking University researchers employed the finite-difference time-domain method to systematically evaluate the two-photo fluorescence behavior of single emitter single nanoshell configuration. Simultaneous excitation and emission enhancements could be achieved by the suitable dimensions of the nanoshell. They found that the emitter located inside or outside the nanoshell at various positions led to significantly different enhancement effect. (as shown in the Figure).
The fluorescent emitter placed outside the nanoshell can achieve large fluorescence intensity given that both the position and orientation of the emission dipole are optimally controlled, but the TPF enhancement decays rapidly with the increase of distance between the emitter and the shell surface. In contrast, for the case of the emitter placed inside the nanoshell, it can experience substantial two-photon fluorescence enhancement without strict requirements upon the position and dipole orientations, the radiative light can be coupled efficiently with the far field. Besides, the metal shell protects the encapsulated fluorophores from the external environment. The stability of fluorophores can be improved by the strong coupling between the fluorophores and the nanoshell resulting in a shorter fluorescence lifetime. These considerations imply that fluorophores encapsulated in metallic nanoshells is a more desirable nanocomposite configuration for the TPF probe in bioimaging applications.
This work provides a comprehensive understanding about the plasmonic-enhanced two-photon fluorescence behaviors, and the nanocomposite configuration has great potential for optical detecting, imaging and sensing in biological applications.
###
The paper's co-authors are Peking University graduate students Zhang Tianyue, Shen Hongming and collaborative scientists Perriat, P.; Martini, M.; Tillement, O. from CNRS, France. This research project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key Basic Research Program of China.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
LU Guowei
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








