Home > Press > Strongly interacting electrons in wacky oxide synchronize to work like the brain
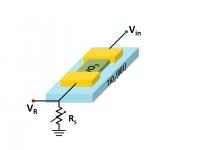 |
| This is a cartoon of an oscillating switch, the basis of a new type of low-power analog computing.
Credit: Credit: Nikhil Shukla, Penn State |
Abstract:
Current computing is based on binary logic -- zeroes and ones -- also called Boolean computing, but a new type of computing architecture stores information in the frequencies and phases of periodic signals and could work more like the human brain using a fraction of the energy necessary for today's computers, according to a team of engineers.
Strongly interacting electrons in wacky oxide synchronize to work like the brain
University Park, PA | Posted on May 15th, 2014Vanadium dioxide is called a "wacky oxide" because it transitions from a conducting metal to an insulating semiconductor and vice versa with the addition of a small amount of heat or electrical current. A device created by electrical engineers at Penn State uses a thin film of vanadium oxide on a titanium dioxide substrate to create an oscillating switch.
Using a standard electrical engineering trick, Nikhil Shukla, graduate student in electrical engineering, added a series resistor to the oxide device to stabilize oscillations over billions of cycles. When Shukla added a second similar oscillating system, he discovered that, over time, the two devices began to oscillate in unison. This coupled system could provide the basis for non-Boolean computing. Shukla worked with Suman Datta, professor of electrical engineering, and co-advisor Roman Engel-Herbert, assistant professor of materials science and engineering, Penn State. They reported their results today (May 14) in Scientific Reports.
"It's called a small-world network," explained Shukla. "You see it in lots of biological systems, such as certain species of fireflies. The males will flash randomly, but then for some unknown reason the flashes synchronize over time."
The brain is also a small-world network of closely clustered nodes that evolved for more efficient information processing.
"Biological synchronization is everywhere," added Datta. "We wanted to use it for a different kind of computing called associative processing, which is an analog rather than digital way to compute."
An array of oscillators can store patterns -- for instance, the color of someone's hair, their height and skin texture. If a second area of oscillators has the same pattern, they will begin to synchronize, and the degree of match can be read out.
"They are doing this sort of thing already digitally, but it consumes tons of energy and lots of transistors," Datta said.
Datta is collaborating with Vijay Narayanan, professor of computer science and engineering, Penn State, in exploring the use of these coupled oscillations to solve visual recognition problems more efficiently than existing embedded vision processors.
Shukla and Datta called on the expertise of Cornell University materials scientist Darrell Schlom to make the vanadium dioxide thin film, which has extremely high quality similar to single crystal silicon. Arijit Raychowdhury, computer engineer, and Abhinav Parihar graduate student, both of Georgia Tech, mathematically simulated the nonlinear dynamics of coupled phase transitions in the vanadium dioxide devices. Parihar created a short video simulation of the transitions, which occur at a rate close to a million times per second, to show the way the oscillations synchronize. Venkatraman Gopalan, professor of materials science and engineering, Penn State, used the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory to visually characterize the structural changes occurring in the oxide thin film in the midst of the oscillations.
Datta believes it will take seven to 10 years to scale up from their current network of two-three coupled oscillators to the 100 million or so closely packed oscillators required to make a neuromorphic computer chip. One of the benefits of the novel device is that it will use only about one percent of the energy of digital computing, allowing for new ways to design computers. Much work remains to determine if vanadium dioxide can be integrated into current silicon wafer technology.
"It's a fundamental building block for a different computing paradigm that is analog rather than digital," said Shukla.
###
Also contributing to this work are Eugene Freeman and Greg Stone, all of Penn State; Haidan Wen and Zhonghou Cai, Argonne National Laboratory; and Hanjong Paik, Cornell University.
The Office of Naval Research primarily supported this work. The National Science Foundation's Expeditions in Computing Award also supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
![]() New study introduces the best graphite films: The work by Distinguished Professor Feng Ding at UNIST has been published in the October 2022 issue of Nature Nanotechnology November 4th, 2022
New study introduces the best graphite films: The work by Distinguished Professor Feng Ding at UNIST has been published in the October 2022 issue of Nature Nanotechnology November 4th, 2022
![]() Thin-film, high-frequency antenna array offers new flexibility for wireless communications November 5th, 2021
Thin-film, high-frequency antenna array offers new flexibility for wireless communications November 5th, 2021
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








