Home > Press > A New Postal Code for Cancer: Freiburg researchers find purely chemical way to target therapeutic nano-containers to cells
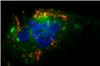 |
| Immunofluorescence image shows nanoparticles targeted to endothelial cells. The red particles turn orange when overlapping with the green caveolin in the lipid rafts of the cells. Source: Julia Voigt / Prasad Shastri |
Abstract:
Scientists have discovered that a polymer can provide a key to get into tumors: Prof. Prasad Shastri, Director of the Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry and core member of the cluster of excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies at the University of Freiburg, and graduate students Julia Voigt and Jon Christensen have developed a new paradigm to home nanoparticles, containers that measure a few 100 nanometers in size, to endothelial cells.
A New Postal Code for Cancer: Freiburg researchers find purely chemical way to target therapeutic nano-containers to cells
Freiburg, Germany | Posted on February 12th, 2014Using just charged polymers with the right affinity for cell lipids the team has developed nanoparticles that can recognize specific cell types simply by their chemical properties. "This is a remarkable discovery, as it allows for the first time to target a specific cell type purely through biophysical principles, and without using the traditional ligand-receptor approach" says Prof. Shastri who led the study. Until now researchers placed molecules on nanoparticles that can latch onto proteins on cell surface - called receptors.
These receptors act as an address or a biological postal code. However in tumors these addresses can change rapidly with time. To solve this lack of precision Shastri and team developed particles that are delivered to endothelial cells using a biophysical approach. "This delivery approach does not require a biological postal code for targeting of nanoparticles and is an important step forward in developing nanoparticle based systems for treating cancers" says Julia Voigt the lead author of the paper.
Cancers are very hungry tissues and they need constant nourishment. This is provided through their own supply of blood vessels. "By going after endothelial cells that make up these blood vessels, we can starve the tumor or kill it with one payload" says Jon Christensen who is a co-author on this study and works on tumor metastasis.
Nanoparticles are used to deliver therapeutics in treating cancers. These very small pills, cornerstones of nanomedicine, get injected into the body and reach the tumor cells via the bloodstream. When they find the targeted cells, they need to be eaten so that the drug can act within the cell. This mechanism is called receptor-mediated endocytosis. Shastri and his team looked to develop a new approach that targets a transport process that is dominant in endothelial cells. It turns out that a structure called caveolae is found in large amounts on endothelial cells. Caveolae are "lipid rafts" on the cell membrane and are one of the doors into the endothelial cells. Prof. Shastri and his team discovered that by decorating nano-pills made of lipids with negatively charged polymers, nanoparticles can preferentially enter through this door. "How exactly these charged polymers enable the nanoparticles to unlock this door we are not sure yet, but we feel confident that with further studies this method could usher in a new approach to delivery of drugs in general" says Shastri. This project was funded by supported by INTERREG and the cluster of excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies.
Full bibliographic information
Julia Voigt, Jon Christensen, V. Prasad Shastri: Differential uptake of nanoparticles by endothelial cells through polyelectrolytes with affinity for caveolae. PNAS Online Early Edition 2014.
####
About Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
The University of Freiburg was founded in 1457 as a classical comprehensive university, making it one of the oldest higher education institutions in Germany. Successful in the Excellence Initiative, the university also boasts an illustrious history with numerous Nobel Prize recipients. Brilliant scholars and creative thinking distinguish it today as a modern top-notch university well equipped for the challenges of the 21st century.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nicolas Scherger
Prof. Dr. V. Prasad Shastri
Institute for Macromolecular Chemistry / BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies
University of Freiburg
Phone: 0761/203-6268
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








