Home > Press > Nanomotors are controlled, for the first time, inside living cells
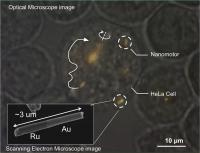 |
| Optical microscope image of a HeLa cell containing several gold-ruthenium nanomotors. Arrows indicate the trajectories of the nanomotors, and the solid white line shows propulsion. Near the center of the image, a spindle of several nanomotors is spinning. Inset: Electron micrograph of a gold-ruthenium nanomotor. The scattering of sound waves from the two ends results in propulsion.
Credit: Mallouk lab, Penn State University |
Abstract:
For the first time, a team of chemists and engineers at Penn State University have placed tiny synthetic motors inside live human cells, propelled them with ultrasonic waves and steered them magnetically. It's not exactly "Fantastic Voyage," but it's close. The nanomotors, which are rocket-shaped metal particles, move around inside the cells, spinning and battering against the cell membrane.
Nanomotors are controlled, for the first time, inside living cells
University Park, PA | Posted on February 10th, 2014"As these nanomotors move around and bump into structures inside the cells, the live cells show internal mechanical responses that no one has seen before," said Tom Mallouk, Evan Pugh Professor of Materials Chemistry and Physics at Penn State. "This research is a vivid demonstration that it may be possible to use synthetic nanomotors to study cell biology in new ways. We might be able to use nanomotors to treat cancer and other diseases by mechanically manipulating cells from the inside. Nanomotors could perform intracellular surgery and deliver drugs noninvasively to living tissues."
The researchers' findings will be published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on 10 February 2014. In addition to Mallouk, co-authors include Penn State researchers Wei Wang, Sixing Li, Suzanne Ahmed, and Tony Jun Huang, as well as Lamar Mair of Weinberg Medical Physics in Maryland U.S.A.
Up until now, Mallouk said, nanomotors have been studied only "in vitro" in a laboratory apparatus, not in living human cells. Chemically powered nanomotors first were developed ten years ago at Penn State by a team that included chemist Ayusman Sen and physicist Vincent Crespi, in addition to Mallouk. "Our first-generation motors required toxic fuels and they would not move in biological fluid, so we couldn't study them in human cells," Mallouk said. "That limitation was a serious problem." When Mallouk and French physicist Mauricio Hoyos discovered that nanomotors could be powered by ultrasonic waves, the door was open to studying the motors in living systems.
For their experiments, the team uses HeLa cells, an immortal line of human cervical cancer cells that typically is used in research studies. These cells ingest the nanomotors, which then move around within the cell tissue, powered by ultrasonic waves. At low ultrasonic power, Mallouk explained, the nanomotors have little effect on the cells. But when the power is increased, the nanomotors spring into action, moving around and bumping into organelles -- structures within a cell that perform specific functions. The nanomotors can act as egg beaters to essentially homogenize the cell's contents, or they can act as battering rams to actually puncture the cell membrane.
While ultrasound pulses control whether the nanomotors spin around or whether they move forward, the researchers can control the motors even further by steering them, using magnetic forces. Mallouk and his colleagues also found that the nanomotors can move autonomously -- independently of one another -- an ability that is important for future applications. "Autonomous motion might help nanomotors selectively destroy the cells that engulf them," Mallouk said. "If you want these motors to seek out and destroy cancer cells, for example, it's better to have them move independently. You don't want a whole mass of them going in one direction."
The ability of nanomotors to affect living cells holds promise for medicine, Mallouk said. "One dream application of ours is Fantastic Voyage-style medicine, where nanomotors would cruise around inside the body, communicating with each other and performing various kinds of diagnoses and therapy. There are lots of applications for controlling particles on this small scale, and understanding how it works is what's driving us."
###
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation (MRSEC grant DMR-0820404), the National Institutes of Health, the Huck Innovative and Transformative Seed Fund (HITS) and Penn State University.
[ Krista Weidner ]
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Barbara K. Kennedy
814-863-4682
Tom Mallouk
(+1) 814 863 9637
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








