Home > Press > Graphene ribbons highly conductive at room temperature
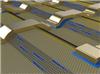 |
| Ballistic graphene ribbons_web.jpg : Conceptual drawing of an electronic circuit comprised of interconnected graphene nanoribbons (black atoms) that are epitaxially grown on steps etched in silicon carbide (yellow atoms). Electrons (blue) travel ballistically along the ribbon and then from one ribbon to the next via the metal contacts. Electron flow is modulated by electrostatic gates © John Hankinson, Georgia Institute of Technology. |
Abstract:
An international team including researchers from CNRS, Université de Lorraine, the SOLEIL synchrotron facility[1], Georgia Institute of technology, Oak Ridge National laboratory and Université de Leibniz have achieved a remarkable feat: they have produced graphene ribbons in which electrons move freely. The scientists have devised an entirely novel way of synthesizing such ribbons, and demonstrated their exceptional electrical conductivity at room temperature. The nanoribbons hold out great promise for cutting-edge electronics. The work is published in the 6 February 2014 issue of the journal Nature.
Graphene ribbons highly conductive at room temperature
Paris, France | Posted on February 7th, 2014Graphene is a material made up of a single layer of atoms that holds tremendous potential. A graphene sheet is around a million times thinner than a hair, more resistant to breakage than steel and yet extremely light. Physically, it takes the form of a honeycomb lattice. When graphene sheets are stacked up, graphite (the grey material in pencil lead) is obtained. In addition, graphene has excellent electrical conductivity: at room temperature, electrons move through it up to 200 times faster than through silicon. Its enormous potential in electronics has triggered much research effort.
A collaboration of physicists from France and the US has been studying the electronic properties of graphene since the early 2000s, with a view to designing a material with very high electron mobility at room temperature. Several years ago, the researchers showed that carbon nanotubes, one of the best-known forms of graphene, can transport electric current ballistically, that is, without encountering resistance within the material. However, carbon nanotubes have proved difficult to manufacture and to insert in large quantities onto electronic chips. As a result, the researchers turned towards another form of graphene: flat ribbons. Similarities in electronic structure between carbon nanotubes and graphene ribbons suggested that they would have analogous conductive properties.
The researchers chose to synthesize this one-dimensional graphene from silicon carbide, a commercially available crystal. Thanks to an ingenious process, they succeeded in obtaining graphene ribbons of very high structural quality, made of an extremely narrow sheet of carbon only 40 nm wide. The main challenge was to ensure that the edges of the ribbon remained highly ordered. This is of paramount importance, since a graphene ribbon with rough edges does not allow good electron propagation. In order to obtain ribbons with regular edges, the trick was to etch nanometer-deep steps into silicon carbide and then produce the graphene ribbons directly on the sidewalls of these steps.
The results exceeded all expectations. The researchers characterized the graphene ribbons produced in this way, which turned out to be ballistic conductors at room temperature: once inside the material, the electrons moved freely without undergoing any scattering. The ribbons thus behaved as waveguides. Charge mobility in these materials exceeded one million cm2/V.s, which would make their electron mobility 1000 times greater than that of the silicon semiconductors (less than 1700 cm2/V.s) used in particular in computer processors and memories. These are the first graphene ribbons to display such conductivity at room temperature.
Another distinctive feature is that the ribbons can be produced easily and in large quantities while keeping the same properties, which makes their large-scale use possible. Because of their exceptional electronic conductivity at room temperature, these new graphene ribbons could find many applications in cutting-edge nanoelectronics.
[1] In France, this work involved the Institut Néel (CNRS) as well as the Institut Jean Lamour (CNRS/Université de Lorraine) and the SOLEIL synchrotron for the characterization of graphene ribbons.
Full bibliographic information
Exceptional ballistic transport in epitaxial graphene nanoribbons. Jens Baringhaus, Ming Ruan, Frederik Edler, Antonio Tejeda, Muriel Sicot, AminaTaleb‐Ibrahimi, An-Pin Li, Zhigang Jiang, Edward Conrad, Claire Berger, Christoph Tegenkamp, Walt A. de Heer. Nature. 6 February 2014.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Julien Guillaume
+ 33 1 44 96 51 51
CNRS researcher
Claire Berger
T + 1 404 894 7880
CNRS Press Officer
Priscilla Dacher
T +33 1 44 96 46 06
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








