Home > Press > Physicists at Mainz University build pilot prototype of a single ion heat engine: Nano-heat engine likely to operate at high efficiency / Publication in Physical Review Letters
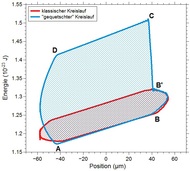 |
| Simulation of an Otto cycle of a single ion heat engine: The enclosed area pictures the produced work that is significantly increased by way of squeezing. |
Abstract:
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg are working on a heat engine that consists of just a single ion. Such a nano-heat engine could be far more efficient than, for example, a car engine or a coal-fired power plant. A usual heat engine transforms heat into utilizable mechanical energy with the corresponding efficiency of an Otto engine amounting to only about 25 percent, for instance. The proposed nano-heat engine consisting of a single calcium ion would be much more efficient. The main aim of the research being conducted is to better understand how thermodynamics works on very small scales. A pilot prototype of such a single-ion heat engine is currently being constructed at Mainz University.
Physicists at Mainz University build pilot prototype of a single ion heat engine: Nano-heat engine likely to operate at high efficiency / Publication in Physical Review Letters
Mainz, Germany | Posted on February 3rd, 2014 As the physicists explain in an article recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the efficiency of heat engines powered by thermal heat reservoirs is determined by the second law of thermodynamics, one of the fundamental concepts in physics. It was as far back as 1824 that Frenchman Nicolas Carnot calculated the maximum possible efficiency limit of such engines, now known as the Carnot limit. In the case of the newly proposed nano-heat engine, the scientists have been theoretically able to exceed the classic Carnot limit by manipulating the heat baths and exploiting nonequlibrium states.
Calculations and simulations made about a year ago showed for the first time that the thermo-dynamic flow in an internal combustion engine could be reproduced using individual ions. The idea was to use a calcium 40 ion, which has a diameter a million times smaller than that of a human hair, for this purpose. "Individual ions can basically act as the piston and drive shaft or, in other words, represent the entire engine," explained Johannes Roßnagel of the Quantum, Atomic, and Neutron Physics (QUANTUM) work group of the JGU Institute of Physics. Individual ions have already been captured in Paul traps and, using laser beams and electrical fields, not only cooled and heated but also compressed. "This means we are able to manipulate the pulse location distribution for optimum efficiency," added Roßnagel. "Exceeding the Carnot limit for a standard heat engine thus does not violate the second law of thermodynamics but instead demonstrates that the use of specially prepared, non-thermal heat reservoirs also makes it possible to further improve efficiency." In their publication, the physicists calculated the general Carnot limit for this situation. As the mechanical capacity of a single ion machine is extremely low, it can probably only be used in heating or cooling nano systems.
The intention is now to actually develop the proposed single ion heat engine in initial experiments and construct a prototype in the laboratory.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Johannes Roßnagel
Quantum, Atomic, and Neutron Physics (QUANTUM)
Institute of Physics
Johannes Gutenberg University
D 55099 Mainz
49-613-139-23671
Fax +49 6131 39-23428
Copyright © Johannes Gutenberg Universitaet Mainz
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








