Home > Press > Turkeys inspire smartphone-capable early warning system for toxins
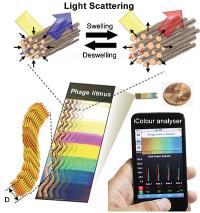 |
| Bio-inspired sensors are made from bacteriophages that mimic the collagen fibers in turkey skin. When exposed to target chemicals, the collagen-like bundles expand or contract, generating different colors. The researchers also created a mobile app to be used with camera phones to help analyze the sensor's color bands.
Credit: Courtesy of the Seung-Wuk Lee Laboratory |
Abstract:
Some may think of turkeys as good for just lunch meat and holiday meals. But bioengineers at the University of California, Berkeley, saw inspiration in the big birds for a new type of biosensor that changes color when exposed to chemical vapors. This feature makes the sensors valuable detectors of toxins or airborne pathogens.
Turkeys inspire smartphone-capable early warning system for toxins
Berkeley, CA | Posted on January 21st, 2014Turkey skin, it turns out, can shift from red to blue to white, thanks to bundles of collagen that are interspersed with a dense array of blood vessels. It is this color-shifting characteristic that gives turkeys the name "seven-faced birds" in Korean and Japanese.
The researchers say that spacing between the collagen fibers changes when the blood vessels swell or contract, depending upon whether the bird is excited or angry. The amount of swelling changes the way light waves are scattered and, in turn, alters the colors we see on the bird's head.
Seung-Wuk Lee, UC Berkeley associate professor of bioengineering, led a research team in mimicking this color-changing ability to create biosensors that can detect volatile chemicals.
"In our lab, we study how light is generated and changes in nature, and then we use what we learn to engineer novel devices," said Lee, who is also a faculty scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
The researchers created a mobile app, called the iColour Analyser, to show that a smartphone photo of the sensor's color bands could be used to help identify toxins of interest. They described their experiments in a study to be published Tuesday, Jan. 21, in the journal Nature Communications.
Sensors that give off color readings are easier to use and read than conventional biosensors. However, the major ones in development elsewhere can only detect a limited range of chemicals and, according to the researchers, they can be very difficult to manufacture.
"Our system is convenient, and it is cheap to make," said Lee. "We also showed that this technology can be adapted so that smartphones can help analyze the color fingerprint of the target chemical. In the future, we could potentially use this same technology to create a breath test to detect cancer and other diseases."
In copying this turkey-skin design, Lee and his team employed a technique they pioneered to mimic nanostructures like collagen fibers. The researchers found a way to get M13 bacteriophages, benign viruses with a shape that closely resembles collagen fibers, to self-assemble into patterns that could be easily fine-tuned.
The researchers found that, like collagen fibers, these phage-bundled nanostructures expanded and contracted, resulting in color changes. The exact mechanism behind the shrinking or expanding phage bundles is still unclear, but it's possible that the small amount of water in the phage is reacting to the chemical vapors, the researchers said.
The turkey-inspired biosensors were exposed to a range of volatile organic compounds, including hexane, isopropyl alcohol and methanol, as well as vapor of the explosive chemical TNT, at concentrations of 300 parts per billion. The researchers found that the viruses swelled rapidly, resulting in specific color patterns that served as "fingerprints" to distinguish the different chemicals tested.
The researchers showed that the biosensor's specificity to a target chemical could be increased by genetically engineering the DNA in the M13 bacteriophage to bind with sites specific to TNT. The biosensor was then exposed to two additional chemicals, DNT and MNT, which have similar molecular structures to TNT. The engineered biosensor successfully distinguished TNT from the other chemicals with distinct color bands.
The biosensors were also able to signal changes in relative humidity, ranging from 20 percent to 90 percent, becoming redder with moister air and bluer with drier air.
The study lead author is Jin-Woo Oh, a former postdoctoral researcher in Lee's lab and now an assistant professor in the Department of Nanomaterial Engineering at Pusan National University in South Korea.
The National Science Foundation, the Defense Acquisition Program Administration and Agency for Defense Development in South Korea, Korea's Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and Samsung helped support this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Yang
510-643-7741
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








