Home > Press > Silver Nanowire Sensors Hold Promise for Prosthetics, Robotics
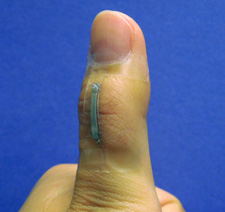 |
| A sensor based on silver nanowires is mounted onto a thumb joint to monitor the skin strain associated with thumb flexing. The sensor shows good wearability and large-strain sensing capability. Photo: Shanshan Yao. |
Abstract:
"Wearable Multifunctional Sensors Using Printed Stretchable Conductors Made Of Silver Nanowires"
Authors: Shanshan Yao and Yong Zhu, North Carolina State University
Published: Online Jan. 14, Nanoscale
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR05496A
Abstract: Considerable efforts have been made to achieve highly sensitive and wearable sensors that can simultaneously detect multiple stimuli such as stretch, pressure, temperature or touch. Here we develop highly stretchable multifunctional sensors that can detect strain (up to 50%), pressure (up to ~1.2 MPa) and finger touch with high sensitivity, fast response time (~40 ms) and good pressure mapping function. The reported sensors utilize the capacitive sensing mechanism, where silver nanowires are used as electrodes (conductors) and Ecoflex is used as a dielectric. The silver nanowire electrodes are screen printed. Our sensors are demonstrated for several wearable applications including monitoring thumb movement, sensing the strain of knee joint in patellar reflex (knee-jerk) and other human motions, illustrating the potential utilities of such sensors in robotic systems, prosthetics, healthcare and flexible touch panels.
Silver Nanowire Sensors Hold Promise for Prosthetics, Robotics
Raleigh, NC | Posted on January 16th, 2014North Carolina State University researchers have used silver nanowires to develop wearable, multifunctional sensors that could be used in biomedical, military or athletic applications, including new prosthetics, robotic systems and flexible touch panels. The sensors can measure strain, pressure, human touch and bioelectronic signals such as electrocardiograms.
"The technology is based on either physical deformation or "fringing" electric field changes. The latter is very similar to the mechanism used in smartphone touch screens, but the sensors we've developed are stretchable and can be mounted on a variety of curvilinear surfaces such as human skin," says Shanshan Yao, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper on the work.
"These sensors could be used to help develop prosthetics that respond to a user's movement and provide feedback when in use," says Dr. Yong Zhu, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State and senior author of the paper. "They could also be used to create robotics that can ‘feel' their environment, or the sensors could be incorporated into clothing to track motion or monitor an individual's physical health."
The researchers built on Zhu's earlier work to create highly conductive and elastic conductors made from silver nanowires. Specifically, the researchers sandwiched an insulating material between two of the stretchable conductors. The two layers then have the ability - called "capacitance" - to store electric charges. Pushing, pulling or touching the stretchable conductors changes the capacitance. The sensors work by measuring that change in capacitance.
"Creating these sensors is simple and low cost," Yao says. "And we've already demonstrated the sensors in several prototype applications."
For example, the researchers employed these sensors to monitor thumb movement, which can be useful in controlling robotic or prosthetic devices. The researchers also demonstrated an application to monitor knee movements while a test subject is running, walking and jumping.
"The deformation involved in these movements is large, and would break a lot of other sensor devices," Zhu says. "But our sensors can be stretched to 150 percent or more of their original length without losing functionality, so they can handle it."
The researchers also developed an array of sensors that can map pressure distribution, which is important for use in robotics and prosthetics applications. The sensors exhibit a quick response time - 40 milliseconds - so strain and pressure can be monitored in real time.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Dr. Yong Zhu
919.513.7735
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








