Home > Press > A micro-muscular breakthrough: Berkeley Lab Researchers Make a Powerful New Microscale Torsional Muscle/Motor from Vanadium Dioxide
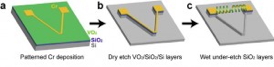 |
| This schematic shows the microfabrication process of a VO2-based bimorph dual coil. |
Abstract:
Vanadium dioxide is poised to join the pantheon of superstars in the materials world. Already prized for its extraordinary ability to change size, shape and physical identity, vanadium dioxide can now add muscle power to its attributes. A team of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has demonstrated a micro-sized robotic torsional muscle/motor made from vanadium dioxide that for its size is a thousand times more powerful than a human muscle, able to catapult objects 50 times heavier than itself over a distance five times its length within 60 milliseconds - faster than the blink of an eye.
This movie shows a vanadium dioxide-based micro-muscle functioning first in micro-catapult mode, throwing out an object, and then in micro-explosion mode, whereby it senses a proximate object and reacts by pushing the object away.
Movie courtesy of Junqiao Wu group, Berkeley Lab/UC Berkeley
A micro-muscular breakthrough: Berkeley Lab Researchers Make a Powerful New Microscale Torsional Muscle/Motor from Vanadium Dioxide
Berkeley, CA | Posted on December 19th, 2013"We've created a micro-bimorph dual coil that functions as a powerful torsional muscle, driven thermally or electro-thermally by the phase transition of vanadium dioxide," says the leader of this work, Junqiao Wu, a physicist who holds joint appointments with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and the University of California-Berkeley's Department of Materials Science and Engineering. "Using a simple design and inorganic materials, we achieve superior performance in power density and speed over the motors and actuators now used in integrated micro-systems."
Wu is the corresponding author of a paper describing this research in the journal Advanced Materials. The paper is titled "Powerful, Multifunctional Torsional Micro Muscles Activated by Phase Transition." Co-authors are Kai Liu, Chun Cheng, Joonki Suh, Robert Tang-Kong, Deyi Fu, Sangwook Lee, Jian Zhou and Leon Chua.
What makes vanadium dioxide highly coveted by the electronics industry is that it is one of the few known materials that's an insulator at low temperatures but abruptly becomes a conductor at 67 degrees Celsius. This temperature-driven phase transition from insulator-to-metal is expected to one day yield faster, more energy efficient electronic and optical devices. However, vanadium dioxide crystals also undergo a temperature-driven structural phase transition whereby when warmed they rapidly contract along one dimension while expanding along the other two. This makes vanadium dioxide an ideal candidate material for creating miniaturized, multi-functional motors and artificial muscles.
"Miniaturizing rotary motors is important for integrated micro-systems and has been intensively pursued over the past decades," Wu says. "The power density of our micro-muscle in combination with its multi-functionality distinguishes it from all current macro- or micro-torsional actuators/motors."
Wu and his colleagues fabricated their micro-muscle on a silicon substrate from a long "V-shaped" bimorph ribbon comprised of chromium and vanadium dioxide. When the V-shaped ribbon is released from the substrate it forms a helix consisting of a dual coil that is connected at either end to chromium electrode pads. Heating the dual coil actuates it, turning it into either a micro-catapult, in which an object held in the coil is hurled when the coil is actuated, or a proximity sensor, in which the remote sensing of an object (meaning without touching it) causes a "micro-explosion," a rapid change in the micro-muscle's resistance and shape that pushes the object away.
"Multiple micro-muscles can be assembled into a micro-robotic system that simulates an active neuromuscular system," Wu says. "The naturally combined functions of proximity sensing and torsional motion allow the device to remotely detect a target and respond by reconfiguring itself to a different shape. This simulates living bodies where neurons sense and deliver stimuli to the muscles and the muscles provide motion."
The vanadium dioxide micro-muscles demonstrated reversible torsional motion over one million cycles with no degradation. They also showed a rotational speed of up to approximately 200,000 rpm, amplitude of 500 to 2,000 degrees per millimeters in length, and an energy power density up to approximately 39 kilowatts/kilogram.
"These metrics are all orders of magnitudes higher than existing torsional motors based on electrostatics, magnetics, carbon nanotubes or piezoelectrics," Wu says.
The heating of the vanadium dioxide micro-muscle to actuate it can be done either globally with a tiny heating pad, or with an electrical current applied to the dual coil. Wu says heating with the electric current is the better way to go because it allows for the selective heating of individual micro-muscles and the heating and cooling process is much faster. In addition, as vanadium dioxide absorbs light and coverts it into heat, the coil can also be triggered optothermally.
"With its combination of power and multi-functionality, our micro-muscle shows great potential for applications that require a high level of functionality integration in a small space," Wu says.
This work was supported by a DOE Office of Science Early Career Award to the University of California, Berkeley.
####
About Berkeley Lab
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world’s most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab’s scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
The DOE Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
510-486-5375
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For more about the research of Junqiao Wu go here:
For more about the research of Junqiao Wu go here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








