Home > Press > UNL-led team finds less is more with adding graphene to nanofibers
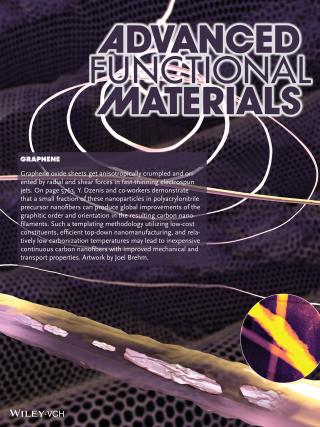 |
| An illustration of the UNL team's research is featured in one of the frontispieces of the Dec. 10 issue of Advanced Functional Materials. |
Abstract:
Figuring that if some is good, more must be better, researchers have been trying to pack more graphene, a supermaterial, into structural composites. Collaborative research led by University of Nebraska-Lincoln materials engineers discovered that, in this case, less is more.
UNL-led team finds less is more with adding graphene to nanofibers
Lincoln, NE | Posted on December 11th, 2013The team, led by Yuris Dzenis, McBroom professor of mechanical and materials engineering and a member of UNL's Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience, learned that using a small amount of graphene oxide as a template improves carbon nanomaterials which, in turn, promises to improve composite materials. Composites are used in everything from airplanes to bicycles and golf clubs.
Graphene is a one-atom thick layer of carbon with a crystalline structure that makes it exceptionally strong and an excellent heat and electrical conductor. It was the subject of research that earned the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics.
UNL engineers collaborated with researchers from Northwestern University and Materials and Electrochemical Research Corp. of Tucson, Ariz., on this study. The UNL team developed a process to incorporate graphene oxide nanoparticles as a template to guide the formation and orientation of continuous carbon nanofibers, which should improve the fiber's properties. That process involves crumpling the graphene, like crumpling a sheet of paper, in a way that improves graphene as a templating and orientation agent. Only small amounts of crumpled graphene nanoparticles are needed. A group led by chemist SonBinh Nguyen of Northwestern synthesized the graphene oxide.
"Many people are trying to put as much graphene as possible into fibers," Dzenis said, adding that it is difficult to do. "But we did the unconventional thing: We used very small quantities followed by carbonization."
The resulting carbon nanofiber structure has an orientation similar to fibers with demonstrated enhanced strength and other properties, Dzenis said. He and his colleagues are now testing their graphene-based nanofibers for these enhanced properties as well as improving the technique.
The method is promising, he said. It could lower the cost of making composites significantly because it requires only small quantities of expensive nanoparticles and uses an inexpensive nanofiber manufacturing process, which was developed at UNL.
"All of this has potential for high-performance but, at the same time, low-cost carbon nanofibers," Dzenis said.
The team reported its findings in the Dec. 10 issue of Advanced Functional Materials. Co-authors are UNL mechanical and materials engineering colleagues Dimitry Papkov and Alexander Goponenko; facilities specialist Xing-Zhong Li of the Nebraska Center for Materials and Nanoscience; Owen C. Compton, Zhi An and SonBinh T. Nguyen of Northwestern; and Alexander Moravsky of Materials and Electrochemical Research Corp.
This research was funded by grants from the U.S. Army Research Office Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative, Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the National Science Foundation.
Writer: Gillian Klucas, Research and Economic Development
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yuris Dzenis
Professor
Mechanical and Materials Engineering
phone: 402-472-0713
Copyright © University of Nebraska–Lincoln
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








