Home > Press > Holistic Cell Design by Berkeley Lab Scientists Leads to High-Performance, Long Cycle-Life Lithium-Sulfur Battery: Battery could find use in mobile applications, and eventually, electric vehicles with 300-mile range
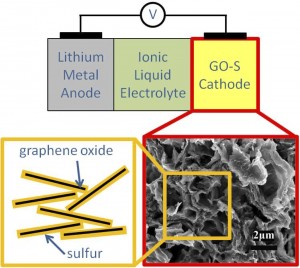 |
| A schematic of a lithium-sulfur battery with SEM photo of silicon-graphene oxide material. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have demonstrated in the laboratory a lithium-sulfur (Li/S) battery that has more than twice the specific energy of lithium-ion batteries, and that lasts for more than 1,500 cycles of charge-discharge with minimal decay of the battery's capacity. This is the longest cycle life reported so far for any lithium-sulfur battery.
Holistic Cell Design by Berkeley Lab Scientists Leads to High-Performance, Long Cycle-Life Lithium-Sulfur Battery: Battery could find use in mobile applications, and eventually, electric vehicles with 300-mile range
Berkeley, CA | Posted on November 20th, 2013Demand for high-performance batteries for electric and hybrid electric vehicles capable of matching the range and power of the combustion engine encourages scientists to develop new battery chemistries that could deliver more power and energy than lithium-ion batteries, currently the best performing battery chemistry in the marketplace.
For electric vehicles to have a 300-mile range, the battery should provide a cell-level specific energy of 350 to 400 Watt-hours/kilogram (Wh/kg). This would require almost double the specific energy (about 200 Wh/kg) of current lithium-ion batteries. The batteries would also need to have at least 1,000, and preferably 1,500 charge-discharge cycles without showing a noticeable power or energy storage capacity loss.
"Our cells may provide a substantial opportunity for the development of zero-emission vehicles with a driving range similar to that of gasoline vehicles," says Elton Cairns, of the Environmental Energy Technologies Division (EETD) at Berkeley Lab.
The battery initially showed an estimated cell-specific energy of more than 500 Wh/kg and it maintained it at >300 Wh/kg after 1,000 cycles—much higher than that of currently available lithium-ion cells.
The team is now seeking support for the continuing development of the Li/S cell, including higher sulfur utilization, operation under extreme conditions, and scale-up. Partnerships with industry are being sought. The next steps in the development are to further increase the cell energy density, improve cell performance under extreme conditions, and scale up to larger cells.
The results were reported in the journal Nano Letters, in a paper authored by Min-Kyu Song (Molecular Foundry, Berkeley Lab), Yuegang Zhang (Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) and Cairns (Environmental Energy Technologies Division, Berkeley Lab). The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science and a University of California Proof of Concept Award.
####
About Berkeley Lab
A U.S. Department of Energy National Laboratory Operated by the University of California
The Molecular Foundry is one of five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers (NSRCs), national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale, supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize, and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE’s Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit science.energy.gov/bes/suf/user-facilities/nanoscale-science-research-centers/.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Allan Chen
510-486-4210
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For a more detailed discussion of the technology, see here:
For a more detailed discussion of the technology, see here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








