Home > Press > Gold nanoparticles give an edge in recycling CO2
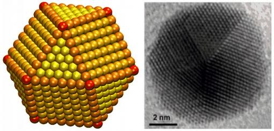 |
| Less is more ... to a point Gold nanoparticles make better catalysts for CO2 recycling than bulk gold metal. Size is crucial though, since edges produce more desired results than corners (red points, above). Nanoparticles of 8 nm appear to have a better edge-to-corner ratio than 4 nm, 6 nm, or 10 nm nanoparticles. Credit: Sun lab/Brown University |
Abstract:
It's a 21st-century alchemist's dream: turning Earth's superabundance of carbon dioxide — a greenhouse gas — into fuel or useful industrial chemicals. Researchers from Brown have shown that finely tuned gold nanoparticles can do the job. The key is maximizing the particles' long edges, which are the active sites for the reaction.
Gold nanoparticles give an edge in recycling CO2
Providence, RI | Posted on October 24th, 2013By tuning gold nanoparticles to just the right size, researchers from Brown University have developed a catalyst that selectively converts carbon dioxide (CO2) to carbon monoxide (CO), an active carbon molecule that can be used to make alternative fuels and commodity chemicals.
"Our study shows potential of carefully designed gold nanoparticles to recycle CO2 into useful forms of carbon," said Shouheng Sun, professor of chemistry and one of the study's senior authors. "The work we've done here is preliminary, but we think there's great potential for this technology to be scaled up for commercial applications."
The findings are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The idea of recycling CO2 — a greenhouse gas the planet current has in excess — is enticing, but there are obstacles. CO2 is an extremely stable molecule that must be reduced to an active form like CO to make it useful. CO is used to make synthetic natural gas, methanol, and other alternative fuels.
Converting CO2 to CO isn't easy. Prior research has shown that catalysts made of gold foil are active for this conversion, but they don't do the job efficiently. The gold tends to react both with the CO2 and with the water in which the CO2 is dissolved, creating hydrogen byproduct rather than the desired CO.
The Brown experimental group, led by Sun and Wenlei Zhu, a graduate student in Sun's group, wanted to see if shrinking the gold down to nanoparticles might make it more selective for CO2. They found that the nanoparticles were indeed more selective, but that the exact size of those particles was important. Eight nanometer particles had the best selectivity, achieving a 90-percent rate of conversion from CO2 to CO. Other sizes the team tested — four, six, and 10 nanometers — didn't perform nearly as well.
"At first, that result was confusing," said Andrew Peterson, professor of engineering and also a senior author on the paper. "As we made the particles smaller we got more activity, but when we went smaller than eight nanometers, we got less activity."
To understand what was happening, Peterson and postdoctoral researcher Ronald Michalsky used a modeling method called density functional theory. They were able to show that the shapes of the particles at different sizes influenced their catalytic properties.
"When you take a sphere and you reduce it to smaller and smaller sizes, you tend to get many more irregular features — flat surfaces, edges and corners," Peterson said. "What we were able to figure out is that the most active sites for converting CO2 to CO are the edge sites, while the corner sites predominantly give the by-product, which is hydrogen. So as you shrink these particles down, you'll hit a point where you start to optimize the activity because you have a high number of these edge sites but still a low number of these corner sites. But if you go too small, the edges start to shrink and you're left with just corners."
Now that they understand exactly what part of the catalyst is active, the researchers are working to further optimize the particles. "There's still a lot of room for improvement," Peterson said. "We're working on new particles that maximize these active sites."
The researchers believe these findings could be an important new avenue for recycling CO2 on a commercial scale.
"Because we're using nanoparticles, we're using a lot less gold than in a bulk metal catalyst," Sun said. "That lowers the cost for making such a catalyst and gives the potential to scale up."
The work was funded by a National Science Foundation grant to the Brown-Yale Center for Chemical Innovation (CCI), which looks for ways to use CO2 as a sustainable feedstock for large-scale commodity chemicals. Other authors on the paper were Önder Metin, Haifeng Lv, Shaojun Guo, Christopher Wright, and Xiaolian Sun.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Stacey
401-863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Chemistry
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








