Home > Press > Stealth nanoparticles lower drug-resistant tumors' defenses
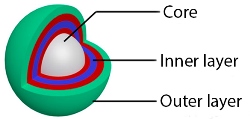 |
| A layered nanoparticle with an anticancer drug core, a gene-silencing inner layer and a tumor-targeting outer layer could provide a new way to attack drug-resistant cancer cells. Credit: American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
Some of the most dangerous cancers are those that can outmaneuver the very drugs designed to defeat them, but researchers are now reporting a new Trojan-horse approach. In a preliminary study in the journal ACS Nano focusing on a type of breast cancer that is highly resistant to current therapies, they describe a way to sneak small particles into tumor cells, lower their defenses and attack them with drugs, potentially making the therapy much more effective.
Stealth nanoparticles lower drug-resistant tumors' defenses
Washington, DC | Posted on October 23rd, 2013Paula T. Hammond and colleagues at the Koch Institute of Integrative Cancer Research at MIT note that triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive disease that is difficult to treat with standard-of-care therapy, and patients' prognoses are poor. These cancer cells evade treatment by ramping up the production of certain proteins that protect tumors from chemotherapy drugs. Interfering with this process could give anticancer drugs a better chance at killing resistant tumors. Recent research into molecules called small interfering RNAs, or siRNAs, is opening doors into possible new treatments using this approach. These molecules can halt the production of particular proteins, so they are ideal candidates for dialing down the levels of protective proteins in tumors. But there are challenges to using siRNAs as part of a cancer therapy, so Hammond's team set out to address them with novel molecular engineering approaches.
They designed a two-stage, "stealth" drug delivery system to attack TNBC cells in mice, often used as stand-ins for humans in research. They created "layer-by-layer" nanoparticles through assembly of components in a certain order around a nano-sized core. An anticancer drug is loaded into the core of the particle, which is then wrapped in a layer of negatively charged siRNA, alternating with positively charged polypeptides, then coated on the outside with a stealthy tumor-targeting shell layer. That layer helps keep the particles in the body long enough for therapy to work. It also allows the particles to specifically bind to TNBC tumor cells. When tested in mice, the nanoparticles targeted the tumors and reduced the levels of protective proteins by nearly 80 percent. With the cancer cells rendered vulnerable, the nanoparticles' anticancer drug payload showed significantly enhanced therapeutic effects and shrunk tumors by 8-fold. The scientists state, "In summary, the results here provide a potential strategy to treat an aggressive and recurrent form of TNBC, as well as a means of adapting this platform to a broad range of controlled multi-drug therapies customizable to the cancer type in a singular nanoparticle delivery system." They also say that the "layer-by-layer" nanoparticle components are biocompatible and biodegradable, which will allow rapid translation into potential clinical benefits.
###
The authors recognize funding from Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the National Cancer Institute, the National Health and Medical Research Council (Australia) the National Science Foundation and the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council (Canada).
####
About American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 163,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Bernstein
202-872-6042
Paula T. Hammond, Ph.D.
Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research
Department of Chemical Engineering
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Rm. 76-553
Cambridge, Mass. 02139
Phone: 617-258-7577
Fax: 617-253-8557
Copyright © American Chemical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








