Home > Press > Tiny antennas let long light waves see in infrared
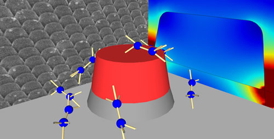 |
| Graphic by Daniel Wasserman
Nanoantennas made of semiconductor can help scientists detect molecules with infrared light. |
Abstract:
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign researchers have developed arrays of tiny nano-antennas that can enable sensing of molecules that resonate in the infrared (IR) spectrum.
Tiny antennas let long light waves see in infrared
Champaign, IL | Posted on September 23rd, 2013
9/23/13
TINY ANTENNAS LET LONG LIGHT WAVES SEE IN INFRARED
CONTACT: Liz Ahlberg, Physical Sciences Editor 217-244-1079;
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign researchers have developed arrays of tiny nano-antennas that can enable sensing of molecules that resonate in the infrared (IR) spectrum.
"The identification of molecules by sensing their unique absorption resonances is very important for environmental monitoring, industrial process control and military applications," said team leader Daniel Wasserman, a professor of electrical and computer engineering. Wasserman is also a part of the Micro and Nano Technology Laboratory at Illinois.
The food and pharmaceutical industries use light to detect contaminants and to ensure quality. The light interacts with the bonds in the molecules, which resonate at particular frequencies, giving each molecule a "spectral fingerprint." Many molecules and materials more strongly resonate in the IR end of the spectrum, which has very long wavelengths of light - often larger than the molecules themselves.
"The absorption signatures of some of the molecules of interest for these applications can be quite weak, and as we move to nano-scale materials, it can be very difficult to see absorption from volumes smaller than the wavelength of light," Wasserman said. "It is here that our antenna array surfaces could have a significant impact."
Other nano-scale antenna systems cannot be tuned to a longer light wavelength because of the limitations of traditional nanoantenna materials. The Illinois team used highly doped semiconductors, grown by a technique called molecular beam epitaxy that is used to make IR lasers and detectors.
"We have shown that nanostructures fabricated from highly doped semiconductors act as antennas in the infrared," said Stephanie Law, a postdoctoral researcher at Illinois and the lead author of the work. "The antennas concentrate this very long wavelength light into ultra-subwavelength volumes, and can be used to sense molecules with very weak absorption resonances."
The semiconductor antenna arrays allow long-wavelength light to strongly interact with nano-scale samples, so the arrays could enhance the detection of small volumes of materials with a standard IR spectrometer - already a commonplace piece of equipment in many industrial and research labs.
The researchers further demonstrated their ability to control the position and strength of the antenna resonance by adjusting the nanoantenna dimensions and the semiconductor material properties.
The group will continue to explore new shapes and structures to further enhance light-matter interaction at very small scales and to potentially integrate these materials with other sensing systems.
"We are looking to integrate these antenna structures with optoelectronic devices to make more efficient, smaller, optoelectronic components for sensing and security applications," Wasserman said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Daniel Wasserman
217-333-9872
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The paper, “All-Semiconductor Plasmonic Nanoantennas for Infrared Sensing,” is available online:
The paper, “All-Semiconductor Plasmonic Nanoantennas for Infrared Sensing,” is available online:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








