Home > Press > New breakthrough for structural characterization of metal nanoparticles
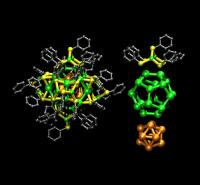 |
| Left: Atomic-scale visualization of the nanoparticle structure with 44 metal sites and 30 thiols. Right: The inner metal core has two shells of 12 and 20 sites (golden and green, respectively), capped by six metal-thiol molecular complexes (one shown on top). Figure credit: Sami Malola, University of Jyväskylä |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Xiamen University in China and the University of Jyväskylä in Finland have characterized a series of stable 1.5 nm metal nanoclusters containing 44 metal atoms, stabilized by 30 organic thiol molecules on the surface. Two types of clusters were synthesized, containing either 44 silver atoms or an intermetallic cluster of 12 gold and 32 silver atoms. The work in the University of Jyväskylä is funded by the Academy of Finland.
New breakthrough for structural characterization of metal nanoparticles
Helsinki, Finland | Posted on September 4th, 2013The special electronic structure of the clusters leads to peaked absorption of radiation in a wide region of ultraviolet and visible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. These novel nanomaterials were synthesized first in 2009 by a group at MIT in the USA, but their atomic structure has not been known until now. This is the first case of a very stable silver-based cluster nanomaterial that can be synthesized in a macroscopic scale, currently of the order of 10 grams from one synthesis. This material is expected to be widely studied for optical, sensing and electron-transfer applications in the future. The results were reported online in Nature Communications on 4 September 2013.
The experimental work was done in Xiamen by the group of Professor Nanfeng Zheng and the computational work by the group of Professor Hannu Häkkinen in the University of Jyväskylä. The other researchers involved were Huayang Yang, Yu Wang and Huaqi Huang in Xiamen University and Lars Gell, Sami Malola and Lauri Lehtovaara in the University of Jyväskylä. The computations were made at the CSC - IT Centre for Science in Espoo, Finland, and at the HRLS-GAUSS Centre in Stuttgart, Germany.
Publication: H. Yang, Y. Wang, H. Huang, L. Gell, L. Lehtovaara, S. Malola, H. Häkkinen and N. Zheng, "All-thiol stabilized Ag44 and Au12Ag32 nanoparticles with single-crystal structures", Nature Communications, published online on 4 September 2013, link: DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3422.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Professor Hannu Häkkinen
358-400-247-973
Professor Nanfeng Zheng,
Leena Vähäkylä
Communications Specialist
Academy of Finland
tel. +358 295 33 5139
+358 40 359 2936
Copyright © Academy of Finland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








