Home > Press > Physicists from Bielefeld University have developed a new method of fabrication
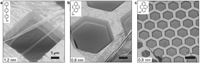 |
| Using a new process the team working with Professor Dr. Armin Gölzhäuser has produced twelve different nanomembranes. The three images were made using the Bielefeld Helium Ion Microscope and show nanomembranes made from various starting materials. Photo: Bielefeld University. |
Abstract:
In the future, carbon nanomembranes are expected to be able to filter out very fine materials. These separating layers are ultrathin, consisting of just one layer of molecules. In the long term, they could allow to separate gases from one another, for example, filtering toxins from the air. At present, the basic research is concerned with the production of nanomembranes. A research team working with Professor Dr. Armin Gölzhäuser of Bielefeld University has succeeded in developing a new path to produce such membranes. The advantage of this procedure is that it allows a variety of different carbon nanomembranes to be generated which are much thinner than conventional membranes. The upcoming issue of the renowned research journal ‘ACS Nano' reports on this research success.
Physicists from Bielefeld University have developed a new method of fabrication
Bielefeld, Germany | Posted on August 22nd, 2013More than ten years ago, Professor Gölzhäuser and his then team created the groundwork for the current development, producing a carbon nanomembrane from biphenyl molecules. In the new study, the process was altered so as to allow the use of other starting materials. The prerequisite is that these molecules are also equipped with several so-called phenyl rings. For their new method, the researchers use the starting material in powder form. They dissolve the powder to pure alcohol and immerse very thin metal layer in this solution. After a short time the dissolved molecules settle themselves on the metal layer to form a monolayer of molecules. After being exposed to electron irradiation, the monolayer becomes a cross-linked nanomembrane. Subsequently the researchers ensure that the metal layer disintegrates, leav-ing only the nanomembrane remaining. ‘Up until now, we have produced small samples which are are a few centimetres square', says Gölzhäuser. ‘However, with this process it is possible to make nanomembranes that are as big as square metres.'
This new method is so special because the researchers can produce made-to-measure nanomembranes. ‘Every starting material has a different property, from thickness or trans-parency to elasticity. By using our process, these characteristics are transferred onto the nanomembrane.' In this way, carbon nanomembranes can be produced to address many dif-ferent needs. ‘That was not possible before now', says Gölzhäuser.
Furthermore, graphene can be made from nanomembranes. Researchers worldwide are ex-pecting graphene to have technically revolutionising properties, as it has an extremely high tensile strength and can conduct electricity and heat very well. The conversion from nanomembranes into graphene is simple for the Bielefeld researchers: The membranes have to be heated in a vacuum at a temperature of about 700 degrees Celsius. Gölzhäuser's team is working on the project with physicists from Ulm University, Frankfurt University and the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research. The study has been funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the German Research Foundation (DFG).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Armin Gölzhäuser
Faculty of Physics
49-521-106-5362
Copyright © University of Bielefeld
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For further information in the Internet, go to:
For further information in the Internet, go to:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








