Home > Press > Chemists develop innovative nano-sensors for multiple proteins: Test strips bearing gold nano-particles as sensor elements can detect numerous proteins simultaneously / New concept with potential applications in medicine, environmental technology, and foodstuff analysis
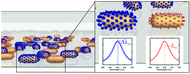 |
| Ill.: Institute of Physical Chemistry When proteins dock with the specifically functionalized nano-particles, the sensor elements change color. |
Abstract:
Chemists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have developed a new method for parallel protein analysis that is, in principle, capable of identifying hundreds or even thousands of different proteins. It could be used to detect the presence of viruses and identify their type in tiny samples. At the same time, it is very cost-effective and quick. "We see possible applications of this technique in medicine, where it could be used, for example, for the rapid diagnosis of a wide range of diseases. It would be almost as easy to use as a pregnancy test strip," said Professor Carsten Sönnichsen of the Institute of Physical Chemistry. The test involves placing a tiny drop of blood, saliva, or other bodily fluid on a small test strip, which is then placed in a device developed at the JGU Institute of Physical Chemistry. This device is able to identify the specific proteins in the fluid and thus allows to quickly and reliably differentiate between harmless microorganisms and dangerous pathogens.
Chemists develop innovative nano-sensors for multiple proteins: Test strips bearing gold nano-particles as sensor elements can detect numerous proteins simultaneously / New concept with potential applications in medicine, environmental technology, and foodstuff analysis
Mainz, Germany | Posted on July 31st, 2013 In order to detect the many different substances present in a small sample, the sensors need to be as tiny as possible, preferably the size of nano-particles. Sönnichsen's team of scientists have designed a sensor no larger than the head of a pin but capable of performing a hundred different individual tests on a surface that is only of one-tenth of a square millimeter in area. The 'test strips' consist of glass capillary tubes that have gold nano-particles as sensor elements on their internal surfaces. "We first prepare our nano-particles using short DNA strands, each of which binds to a specific type of protein," explained Janak Prasad, who developed the functionalization method. When a protein docks with one of these special DNA strands, called aptamers, the corresponding nano-particle changes its color. The color changes can be detected with the aid of a spectrometer. For this purpose, the capillary tubes are placed under a microscope designed, constructed, and provided with the necessary software by the Mainz-based team of chemists.
"We demonstrate a new approach for a multiplexed assay that detects multiple proteins simultaneously by letting a fluid flow past the randomly positioned gold nano-rods," explained Christina Rosman, first author of the study. The team from JGU's Institute of Physical Chemistry used four different target proteins to demonstrate the viability of the new concept, its ability to detect concentrations in the nanomolar range, and the possibility to recycle the sensors for more than one analysis. "We see the potential to extend our method to the simultaneous detection of hundreds or even thousands of different target substances," assert the authors in their article published in the June 2013 issue of the journal Nano Letters. Low-cost serial production of the sensors is feasible if advanced nano-fabrication methods such as nano-printing or optical trapping are used.
There are manifold possible applications of a test for multiple targets in a single procedure. The low-cost sensors could be directly used by physicians in their practices in order to detect and discriminate various types of flu viruses with which their patients could be infected. In addition, the technique would also be suitable for detecting the presence of toxins in the environment or in food, particularly in liquids such as milk or baby food, or the presence of doping or other illicit drugs.
Support for the research on this novel multiplexed protein sensor was provided by the Graduate School of Excellence 'Materials Science in Mainz' (MAINZ) and the European Research Council (ERC) 'Single Sense' project.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Carsten Sönnichsen
Institute of Physical Chemistry
Johannes Gutenberg University
D 55099 Mainz
Tel +49 6131 39-24313
Fax +49 6131 39-26747
49-613-139-24313
Copyright © Johannes Gutenberg Universitaet Mainz
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








