Home > Press > A new way to trap light: MIT researchers discover a new phenomenon that could lead to new types of lasers and sensors
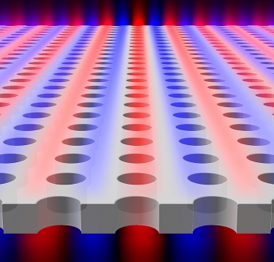 |
| Light is found to be confined within a planar slab with periodic array of holes, although the light is theoretically "allowed" to escape. Blue and red colors indicate surfaces of equal electric field. Image: Chia Wei Hsu |
Abstract:
There are several ways to "trap" a beam of light — usually with mirrors, other reflective surfaces, or high-tech materials such as photonic crystals. But now researchers at MIT have discovered a new method to trap light that could find a wide variety of applications.
A new way to trap light: MIT researchers discover a new phenomenon that could lead to new types of lasers and sensors
Cambridge, MA | Posted on July 10th, 2013The new system, devised through computer modeling and then demonstrated experimentally, pits light waves against light waves: It sets up two waves that have the same wavelength, but exactly opposite phases — where one wave has a peak, the other has a trough — so that the waves cancel each other out. Meanwhile, light of other wavelengths (or colors) can pass through freely.
The researchers say that this phenomenon could apply to any type of wave: sound waves, radio waves, electrons (whose behavior can be described by wave equations), and even waves in water.
The discovery is reported this week in the journal Nature by professors of physics Marin Soljačić and John Joannopoulos, associate professor of applied mathematics Steven Johnson, and graduate students Chia Wei Hsu, Bo Zhen, Jeongwon Lee and Song-Liang Chua.
"For many optical devices you want to build," Soljačić says — including lasers, solar cells and fiber optics — "you need a way to confine light." This has most often been accomplished using mirrors of various kinds, including both traditional mirrors and more advanced dielectric mirrors, as well as exotic photonic crystals and devices that rely on a phenomenon called Anderson localization. In all of these cases, light's passage is blocked: In physics terminology, there are no "permitted" states for the light to continue on its path, so it is forced into a reflection.
In the new system, however, that is not the case. Instead, light of a particular wavelength is blocked by destructive interference from other waves that are precisely out of phase. "It's a very different way of confining light," Soljačić says.
While there may ultimately be practical applications, at this point the team is focused on its discovery of a new, unexpected phenomenon. "New physical phenomena often enable new applications," Hsu says. Possible applications, he suggests, could include large-area lasers and chemical or biological sensors.
The researchers first saw the possibility of this phenomenon through numerical simulations; the prediction was then verified experimentally.
In mathematical terms, the new phenomenon — where one frequency of light is trapped while other nearby frequencies are not — is an example of an "embedded eigenvalue." This had been described as a theoretical possibility by the mathematician and computational pioneer John von Neumann in 1929. While physicists have since been interested in the possibility of such an effect, nobody had previously seen this phenomenon in practice, except for special cases involving symmetry.
Written by David Chandler, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
671-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








