Home > Press > An Innovative material for the Green Earth: Simple and inexpensive process to make a material for CO2 adsorption
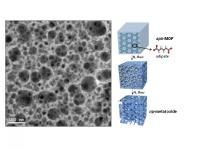 |
| (Left)It shows TEM image of np-MgO-500. (Right) This is the schematic view of the direct conversion from aph-MOG to np-metal oxide by heating under nitrogen atmosphere.
Credit: UNIST |
Abstract:
Researchers from Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), S. Korea, developed a novel, simple method to synthesize hierarchically nanoporous frameworks of nanocrystalline metal oxides such as magnesia and ceria by the thermal conversion of well-designed metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
An Innovative material for the Green Earth: Simple and inexpensive process to make a material for CO2 adsorption
Ulsan, South Korea | Posted on June 17th, 2013The novel material developed by the UNIST research team has exceptionally high CO2 adsorption capacity which could pave the way to save the Earth from CO2 pollution.
Nanoporous materials consist of organic or inorganic frameworks with a regular, porous structure. Because of their uniform pore sizes they have the property of letting only certain substances pass through, while blocking others. Nanoporous metal oxide materials are ubiquitous in materials science because of their numerous potential applications in various areas, including adsorption, catalysis, energy conversion and storage, optoelectronics, and drug delivery. While synthetic strategies for the preparation of siliceous nanoporous materials are well-established, non-siliceous metal oxide-based nanoporous materials still present challenges.
A description of the new research was published (Web) on May 7 in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. (Title: Nanoporous Metal Oxides with Tunable and Nanocrystalline Frameworks via Conversion of Metal-Organic Frameworks) This article will be also highlighted in the Editor's Choice of the journal Science.
Leading the research team was married couple Hoi Ri Moon and Sang Hoon Joo, both assistant professors at UNIST, who contributed to synthesizing nanoporous metal oxides and characterizing nanoporous materials respectively. Fellow authors include Tae Kyung Kim, Kyung Joo Lee, Jae Yeong Cheon and Jae Hwa Lee from UNIST.
The UNIST research team used MOFs based on aliphatic carboxylate ligands which are thermally less stable and much more labile than aromatic ligands. Specifically, the aliphatic ligand is adipic acid, which is a precursor for the production of nylon, and thus very important from an industrial perspective and low in price. During the thermolysis of a crystalline, aliphatic carboxylate ligand-based MOF (aph-MOF), the ligands were transformed into organic moieties via chemical decomposition, and were confined as vesicles in the solids.
The organic vesicles acted as self-generated porogens, which later were converted into nanopores; they also prevented aggregation of the metal oxide nanocrystals. Finally, upon thermolysis at higher temperature, the confined organic moieties evaporated, generating highly porous nanostructures comprising nanocrystalline metal oxides. The control of the retention time and the evaporation rate of the organic moieties in the host solid were critical for the successful formation of nanoporous metal oxides with nanocrystalline frameworks. The thermal treatments converted the Mg-aph-MOF into 3-dimensionally nanoporous MgO frameworks instead of discrete MgO nanoparticles embedded in a carbon matrix. Significantly, nanoporous MgO exhibited exceptional CO2 adsorption capacity (9.2 wt %) under conditions mimicking flue gas.
"I believe MOF-driven strategy can be expanded to other nanoporous monometallic and multimetallic oxides with a multitude of potential applications, especially for energy-related materials" said Prof. Moon. "Because of its high CO2 adsorption capacity, it will open a new way for environmental solutions."
"Various metal oxides converted from well-designed MOFs are being studied as fuel cell catalysts, also" said Prof. Joo, explaining his future research plan.
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Eunhee Song
82-522-171-224
Copyright © Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology(UNIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Homepage of Prof. Hoi Ri Moon:
Homepage of Prof. Hoi Ri Moon:
![]() Homepage of Prof. Sang Hoon Joo:
Homepage of Prof. Sang Hoon Joo:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








