Home > Press > Nanotechnology helps track and improve drug action in pancreatic cancer
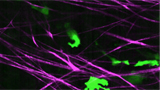 |
| Cancer cells (green) spreading through tissue surrounding a tumour |
Abstract:
UK and Australian scientists have been able to show ways in which we can markedly improve drug targeting of solid tumours, using tiny ‘biosensors' along with new advanced imaging techniques.
Nanotechnology helps track and improve drug action in pancreatic cancer
Sydney, Australia | Posted on June 13th, 2013In real time and in three dimensions, these technologies can show us how cancers spread and how active cancer cells respond to a particular drug. They can also tell us how much, how often and how long to administer drugs. Finally, using preclinical models of the disease, they can guide the use of ‘combination therapies', techniques that enhance drug delivery by breaking up the tissue surrounding a tumour.
The study was performed by Dr Paul Timpson of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and Professor Kurt Anderson of the Beatson Institute for Cancer Research in Glasgow, UK. PhD student Max Nobis studied the signaling protein ‘Src', which becomes activated to drive invasive pancreatic cancer, and looked at how it could best be deactivated by a small molecule inhibitor — currently in phase II clinical trials — known as ‘dasatinib'. Their findings are published in the journal Cancer Research, now online.
"We have already shown that Src is activated in pancreatic tumours and we knew that dasatinib deactivates Src and could partially reduce the spread of this form of cancer. Through a collaborative partner in the US, we had access to FRET (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) imaging technology," said Dr Paul Timpson.
"Until now, we have been limited to studying tumour signalling in two dimensions - and lacked a dynamic way of reporting on drug targeting in live tumour tissue. Nanotechnology opens up a portal into living tissue that allows us to watch cancers spreading, and to determine which parts of a tumour we should be targeting with drugs."
"This imaging technology has allowed us to map areas within the tumour that are highly aggressive, allowing us to pinpoint regions of poor drug delivery deep within a tumour at sub-cellular resolution. We can then see where we need to improve on drug delivery to improve clinical outcome."
It has been hard to treat pancreatic tumours because they are extremely dense with collagen and have poor blood vessel networks for delivering drugs.
Professor Kurt Anderson observed that combination therapies can now be used to break down collagen, weakening tumour architecture and making it easier to get the drugs where they need to be. "The trick is to break down the structure just enough to get the drug in, but not so much that you damage the organ itself," he said.
"These new FRET technologies help us gauge what is just enough and not too much."
"These are very exciting discoveries - we now have spatial and temporal information about cancer behaviour that we've never had before, as well as the nanotechnology to monitor and improve drug delivery in hard to reach tumour regions."
####
About Garvan Institute of Medical Research
The Garvan Institute of Medical Research was founded in 1963. Initially a research department of St Vincent's Hospital in Sydney, it is now one of Australia's largest medical research institutions with over 600 scientists, students and support staff. Garvan's main research areas are: Cancer, Diabetes & Obesity, Immunology and Inflammation, Osteoporosis and Bone Biology and Neuroscience. Garvan's mission is to make significant contributions to medical science that will change the directions of science and medicine and have major impacts on human health. The outcome of Garvan's discoveries is the development of better methods of diagnosis, treatment, and ultimately, prevention of disease.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alison Heather
Science Communications Manager
M: + 61 434 071 326
61-292-958-128
Copyright © Garvan Institute of Medical Research
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








