Home > Press > The Diabetes ‘Breathalyzer’: Pitt chemists demonstrate sensor technology that could detect and monitor diabetes through breath analysis alone
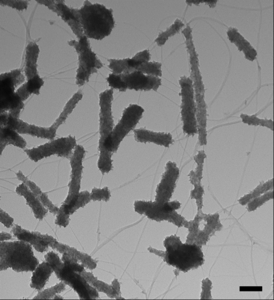 |
| A transmission electron microscopy image of the hybrid material revealing the formation of “titanium dioxide on a stick.” |
Abstract:
Diabetes patients often receive their diagnosis after a series of glucose-related blood tests in hospital settings, and then have to monitor their condition daily through expensive, invasive methods. But what if diabetes could be diagnosed and monitored through cheaper, noninvasive methods?
The Diabetes ‘Breathalyzer’: Pitt chemists demonstrate sensor technology that could detect and monitor diabetes through breath analysis alone
Pittsburgh, PA | Posted on June 10th, 2013Chemists at the University of Pittsburgh have demonstrated a sensor technology that could significantly simplify the diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes through breath analysis alone. Their findings were published in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Even before blood tests are administered, those with diabetes often recognize the condition's symptoms through their breath acetone—a characteristic "fruity" odor that increases significantly with high glucose levels. The Pitt team was interested in this biomarker as a possible diagnostic tool.
"Once patients are diagnosed with diabetes, they have to monitor their condition for the rest of their lives," said Alexander Star, principal investigator of the project and Pitt associate professor of chemistry. "Current monitoring devices are mostly based on blood glucose analysis, so the development of alternative devices that are noninvasive, inexpensive, and provide easy-to-use breath analysis could completely change the paradigm of self-monitoring diabetes."
Together with his colleagues—Dan Sorescu, a research physicist at the National Energy Technology Laboratory, and Mengning Ding, a Pitt graduate student studying chemistry—Star used what's called a "sol-gel approach," a method for using small molecules (often on a nanoscale level) to produce solid materials. The team combined titanium dioxide—an inorganic compound widely used in body-care products such as makeup—with carbon nanotubes, which acted as "skewers" to hold the particles together. These nanotubes were used because they are stronger than steel and smaller than any element of silicon-based electronics.
This method, which the researchers playfully call "titanium dioxide on a stick," effectively combined the electrical properties of the tubes with the light-illuminating powers of the titanium dioxide. They then created the sensor device by using these materials as an electrical semiconductor, measuring its electrical resistance (the sensor's signal).
The researchers found the sensor could be activated with light to produce an electrical charge. This prompted them to "cook" the "skewers" in the sensor under ultraviolet light to measure acetone vapors—which they found were lower than previously reported sensitivities.
"Our measurements have excellent detection capabilities," said Star. "If such a sensor could be developed and commercialized, it could transform the way patients with diabetes monitor their glucose levels."
The team is currently working on a prototype of the sensor, with plans to test it on human breath samples soon.
The paper, "Photoinduced Charge Transfer and Acetone Sensitivity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Titanium Dioxide Hybrids," was first published in JACS online June 5. The work was performed in support of ongoing research at the National Energy Technology Laboratory.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
B. Rose Huber
412-624-4356
Cell: 412-328-6008
Copyright © University of Pittsburgh
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








