Home > Press > Anasys reports on University of Illinois study of near-field behavior of semiconductor plasmonic microparticles using AFM-IR published in APL
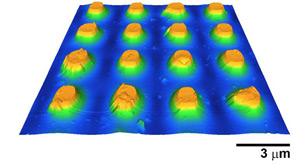 |
| An atomic force microscope image of plasmonic semiconductor microparticles |
Abstract:
Anasys Instruments reports on the announcement from the University of Illinois which describes the effect of nanometer-scale heating on semiconductor plasmonic microparticles which reveal surface plasmon resonance. The work is described in a paper published in Applied Physics Letters.
Anasys reports on University of Illinois study of near-field behavior of semiconductor plasmonic microparticles using AFM-IR published in APL
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on May 14th, 2013Recent progress in the engineering of plasmonic structures has enabled new kinds of nanometer-scale optoelectronic devices as well as high-resolution optical sensing. But until now, there has been a lack of tools for measuring nanometer-scale behavior in plasmonic structures which are needed to understand device performance and to confirm theoretical models.
"For the first time, we have measured nanometer-scale infrared absorption in semiconductor plasmonic microparticles using a technique that combines atomic force microscopy with infrared spectroscopy," explained William P King, an Abel Bliss Professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering (MechSE) at Illinois. "Atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy (AFM-IR*) allows us to directly observe the plasmonic behavior within microparticle infrared antennas."
The article describing the research, "Near-field infrared absorption of plasmonic semiconductor microparticles studied using atomic force microscope infrared spectroscopy," appears in Applied Physics Letters.
"Highly doped semiconductors can serve as wavelength flexible plasmonic metals in the infrared," noted Daniel M Wasserman, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Illinois. "However, without the ability to visualize the optical response in the vicinity of the plasmonic particles, we can only infer the near-field behavior of the structures from their far-field response. What this work gives us is a clear window into the optical behavior of this new class of materials on a length scale much smaller than the wavelength of light."
The article compares near-field and far-field measurements with electromagnetic simulations to confirm the presence of localized plasmonic resonance. The article further reports high resolution maps of the spatial distribution of absorption within single plasmonic structures and variation across plasmonic arrays.
"The ability to measure near field behavior in plasmonic structures allows us to begin expanding our design parameters for plasmonic materials," commented Jonathan Felts, a MechSE graduate student. "Now that we can measure the optical behavior of individual features, we can start to think about designing and testing more complex optical materials."
The authors on the research are Jonathan Felts, Stephanie Law, Daniel M Wasserman, and William P King of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, along with Christopher M Roberts and Viktor Podolskiy of the University of Massachusetts. The article is available online. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation.
*AFM-IR is a product from Anasys Instruments, Inc. For more information on AFM-IR and its applications, please visit the Anasys web site: www.anasysinstruments.com.
####
About Anasys Instruments
Anasys Instruments is dedicated to delivering innovative products that measure material properties for samples with spatially varying physical and chemical properties at the nanoscale. Anasys introduced the nano-TA in 2006 which pioneered the field of nanoscale thermal property measurement. In 2010, Anasys introduced the award-winning breakthrough nanoIR™ Platform which pioneered the field of nanoscale IR measurement. Most recently, Anasys is proud to introduce the breakthrough Lorentz Force Contact Resonance, which pioneers the field of wideband nanomechanical spectroscopy.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anasys contact:
Roshan Shetty
Anasys Instruments Corporation
121 Gray Avenue, Suite 100
Santa Barbara
CA 93101 USA
Tel: +1 (805) 730-3310
www.anasysinstruments.com
Media contact:
Jezz Leckenby
Talking Science Limited
39 de Bohun Court
Saffron Walden
Essex CB10 2BA, UK
Tel +44 (0) 1799 521881
Mob +44 (0) 7843 012997
www.talking-science.com
Copyright © Anasys Instruments
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








