Home > Press > New material approach should increase solar cell efficiency
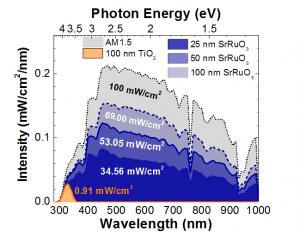 |
| The correlated electron metal SrRuO3 exhibits strong visible slight absorption. Overlaid here on the AM1.5G solar spectrum, it can be seen that SrRuO3 absorbs more than 75 times more light than TiO2. The structural, chemical, and electronic compatibility of TiO2 and SrRuO3 further enables the fabrication of heterojunctions with exciting photovoltaic and photocatalytic response driven by hot-carrier injection. |
Abstract:
"When designing next generation solar energy conversion systems, we must first develop ways to more efficiently utilize the solar spectrum," explained Lane Martin, whose research group has done just that.
"This is a fundamentally new way of approaching these matters," said Martin, who is an assistant professor of materials science and engineering (MatSE) at Illinois. "From these materials we can imagine carbon-neutral energy production of clean-burning fuels, waste water purification and remediation, and much more."
New material approach should increase solar cell efficiency
Urbana, IL | Posted on April 23rd, 2013Martin's research group brought together aspects of condensed matter physics, semiconductor device engineering, and photochemistry to develop a new form of high-performance solar photocatalyst based on the combination of the TiO2 (titanium dioxide) and other "metallic" oxides that greatly enhance the visible light absorption and promote more efficient utilization of the solar spectrum for energy applications. Their paper, "Strong Visible-Light Absorption and Hot-Carrier Injection in TiO2/SrRuO3 Heterostructures," appears in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.
According to Martin, the primary feature limiting the performance of oxide-based photovoltaic and/or photocatalytic systems has traditionally been the poor absorption of visible light in these often wide band gap materials. One candidate oxide material for such applications is anatase TiO2, which is arguably the most widely-studied photocatalyst due to its chemical stability, non-toxicity, low-cost, and excellent band alignment to several oxidation-reduction reactions. As the backbone of dye-sensitized solar cells, however, the presence of a light-absorbing dye accounts for a large band gap which limits efficient usage of all but the UV portion of sunlight.
"We observed that the unusual electronic structure of SrRuO3 is also responsible for unexpected optical properties including high absorption across the visible spectrum and low reflection compared to traditional metals," stated Sungki Lee, the paper's first author. "By coupling this material to TiO2 we demonstrate enhanced visible light absorption and large photocatalytic activities."
"SrRuO3 is a correlated electron oxide which is known to possess metallic-like temperature dependence of its resistivity and itinerant ferromagnetism and for its widespread utility as a conducting electrode in oxide heterostructures," Lee added. Referring to this material as a "metal," however, is likely inappropriate as the electronic structure and properties are derived from a combination of complex electronic density of states, electron correlations, and more.
Using a process called photo-excited hot-carrier injection from the SrRuO3 to the TiO2, the researchers created new heterostructures whose novel optical properties and the resulting high photoelectrochemical performance provide an interesting new approach that could advance the field of photocatalysis and further broaden the potential applications of other metallic oxides.
This work provides an exciting new approach to the challenge of designing visible-light photosensitive materials and has resulted in a provisional patent application. The work was primarily supported by the ongoing International Institute for Carbon Neutral Energy Research (I2CNER) program, a partnership between Kyushu University in Japan and the University of Illinois.
"The I2CNER project brings together some of the leading energy researchers from around the globe," explained I2CNER Director Petros Sofronis, who is also a professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois. "Results from Dr. Martin's research group and others demonstrate that I2CNER is not only an experiment on international collaboration. It is a concerted institutionalized effort to pursue green innovation and reduced CO2 emissions, as well as to advance fundamental science and develop science-based technological solutions for the reorganization of sustainable and environmentally friendly society."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lane Martin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
217/244-9162
Petros Sofronis
director
International Institute for Carbon Neutral Energy Research
217/333-2636
Writer:
Rick Kubetz
Engineering Communications Office
217/244-7716
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








