Home > Press > Record simulations conducted on Lawrence Livermore supercomputer
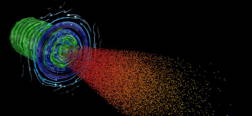 |
| OSIRIS simulation on Sequoia of the interaction of a fast-ignition-scale laser with a dense DT plasma. The laser field is shown in green, the blue arrows illustrate the magnetic field lines at the plasma interface and the red/yellow spheres are the laser-accelerated electrons that will heat and ignite the fuel. |
Abstract:
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have performed record simulations using all 1,572,864 cores of Sequoia, the largest supercomputer in the world. Sequoia, based on IBM BlueGene/Q architecture, is the first machine to exceed one million computational cores. It also is No. 2 on the list of the world's fastest supercomputers, operating at 16.3 petaflops (16.3 quadrillion floating point operations per second).
Record simulations conducted on Lawrence Livermore supercomputer
Livermore, CA | Posted on March 19th, 2013The simulations are the largest particle-in-cell (PIC) code simulations by number of cores ever performed. PIC simulations are used extensively in plasma physics to model the motion of the charged particles, and the electromagnetic interactions between them, that make up ionized matter. High performance computers such as Sequoia enable these codes to follow the simultaneous evolution of tens of billions to trillions of individual particles in highly complex systems.
Frederico Fiuza, a physicist and Lawrence Fellow at LLNL, performed the simulations in order to study the interaction of ultra-powerful lasers with dense plasmas in a proposed method to produce fusion energy, the energy source that powers the sun, in a laboratory setting. The method, known as fast ignition, uses lasers capable of delivering more than a petawatt of power (a million billion watts) in a fraction of a billionth of a second to heat compressed deuterium and tritium (DT) fuel to temperatures exceeding the 50 million degrees Celsius needed to initiate fusion reactions and release net energy. The project is part of the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Fusion Energy Science Program.
This method differs from the approach being taken by LLNL's National Ignition Facility to achieve thermonuclear ignition and burn. NIF's approach is called the "central hot spot" scenario, which relies on simultaneous compression and ignition of a spherical fuel capsule in an implosion, much like in a diesel engine. Fast ignition uses the same hardware as the hot spot approach but adds a high-intensity, ultrashort-pulse laser as the "spark" that achieves ignition.
The code used in these simulations was OSIRIS, a PIC code that has been developed over more than 10 years in a collaboration between the University of California, Los Angeles and Portugal's Instituto Superior Técnico. Using this code, Fiuza demonstrated excellent scaling in parallel performance of OSIRIS to the full 1.6 million cores of Sequoia. By increasing the number of cores for a relatively small problem of fixed size, what computer scientists call "strong scaling," OSIRIS obtained 75 percent efficiency on the full machine. But when the total problem size was increased, what is called "weak scaling," a 97 percent efficiency was achieved.
"This means that a simulation that would take an entire year to perform on a medium-size cluster of 4,000 cores can be performed in a single day. Alternatively, problems 400 times greater in size can be simulated in the same amount of time," Fiuza said. "The combination of this unique supercomputer and this highly efficient and scalable code is allowing for transformative research."
OSIRIS is routinely used for fundamental science during the test phase of Sequoia in simulations with up to 256,000 cores. These simulations are allowing researchers, for the first time, to model the interaction of realistic fast-ignition-scale lasers with dense plasmas in three dimensions with sufficient speed to explore a large parameter space and optimize the design for ignition. Each simulation evolves the dynamics of more than 100 billion particles for more than 100,000 computational time steps. This is approximately an order of magnitude larger than the previous largest simulations of fast ignition.
Sequoia is a National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) machine, developed and fielded as part of NNSA's Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) program. Sequoia is preparing to move to classified computing in support of stockpile stewardship.
"This historic calculation is an impressive demonstration of the power of high-performance computing to advance our scientific understanding of complex systems," said Bill Goldstein, LLNL's deputy director for Science and Technology. "With simulations like this, we can help transform the outlook for laboratory fusion as a tool for science, energy and stewardship of the nuclear stockpile."
####
About Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Breanna Bishop
925-423-9802
Copyright © Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








