Home > Press > UC Santa Barbara Scientists Develop A Whole New Way of Harvesting Energy from the Sun
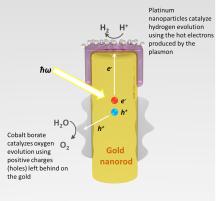 |
| The process by which light is captured by the gold nanorod, and converted into energy that can spilt water (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen. Credit: Syed Mubeen |
Abstract:
A new method of harvesting the Sun's energy is emerging, thanks to scientists at UC Santa Barbara's Departments of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering, and Materials. Though still in its infancy, the research promises to convert sunlight into energy using a process based on metals that are more robust than many of the semiconductors used in conventional methods. The researchers' findings are published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
UC Santa Barbara Scientists Develop A Whole New Way of Harvesting Energy from the Sun
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on February 25th, 2013 "It is the first radically new and potentially workable alternative to semiconductor-based solar conversion devices to be developed in the past 70 years or so," said Martin Moskovits, professor of chemistry at UCSB.
In conventional photoprocesses, a technology developed and used over the last century, sunlight hits the surface of semiconductor material, one side of which is electron-rich, while the other side is not. The photon, or light particle, excites the electrons, causing them to leave their postions, and create positively-charged "holes." The result is a current of charged particles that can be captured and delivered for various uses, including powering lightbulbs, charging batteries, or facilitating chemical reactions.
"For example, the electrons might cause hydrogen ions in water to be converted into hydrogen, a fuel, while the holes produce oxygen," said Moskovits.
In the technology developed by Moskovits and his team, it is not semiconductor materials that provide the electrons and venue for the conversion of solar energy, but nanostructured metals -- a "forest" of gold nanorods, to be specific.
For this experiment, gold nanorods were capped with a layer of crystalline titanium dioxide decorated with platinum nanoparticles, and set in water. A cobalt-based oxidation catalyst was deposited on the lower portion of the array.
"When nanostructures, such as nanorods, of certain metals are exposed to visible light, the conduction electrons of the metal can be caused to oscillate collectively, absorbing a great deal of the light," said Moskovits. "This excitation is called a surface plasmon."
As the "hot" electrons in these plasmonic waves are excited by light particles, some travel up the nanorod, through a filter layer of crystalline titanium dioxide, and are captured by platinum particles. This causes the reaction that splits hydrogen ions from the bond that forms water. Meanwhile, the holes left behind by the excited electrons head toward the cobalt-based catalyst on the lower part of the rod to form oxygen.
According to the study, hydrogen production was clearly observable after about two hours. Additionally, the nanorods were not subject to the photocorrosion that often causes traditional semiconductor material to fail in minutes.
"The device operated with no hint of failure for many weeks," Moskovits said.
The plasmonic method of splitting water is currently less efficient and more costly than conventional photoprocesses, but if the last century of photovoltaic technology has shown anything, it is that continued research will improve on the cost and efficiency of this new method -- and likely in far less time than it took for the semiconductor-based technology, said Moskovits.
"Despite the recentness of the discovery, we have already attained ‘respectable' efficiencies. More importantly, we can imagine achievable strategies for improving the efficiencies radically," he said.
Research in this study was also performed by postdoctoral researchers Syed Mubeen and Joun Lee; grad student Nirala Singh; materials engineer Stephan Kraemer; and chemistry professor Galen Stucky.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sonia Fernandez
(805) 637-3726
George Foulsham
(805) 893-3071
Copyright © University of California - Santa Barbara
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








