Home > Press > Black silicon can take efficiency of solar cells to new levels
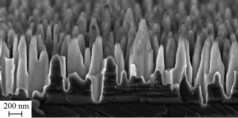 |
| SEM image of the Al2O3 coated CZ Si surface with b-Si where a thin Al2O3 layer can be seen on top of the nanostructure. |
Abstract:
Scientists at Aalto University, Finland, have demonstrated results that show a huge improvement in the light absorption and the surface passivation on silicon nanostructures. This has been achieved by applying atomic layer coating. The results advance the development of devices that require high sensitivity light response such as high efficiency solar cells.
Black silicon can take efficiency of solar cells to new levels
Aalto, Finland | Posted on January 19th, 2013- This method provides extremely good surface passivation. Simultaneously, it reduces the reflectance further at all wavelengths. These results are very promising considering the use of black silicon (b-Si) surfaces on solar cells to increase the efficiency to completely new levels, tells Päivikki Repo, a researcher at Aalto University.
More effective surface passivation methods than those used in the past have been needed to make black silicon a viable material for commercial applications. Good surface passivation is crucial in photonic applications such as solar cells. So far, the poor charge carrier transport properties attributed to nanostructured surfaces have been more detrimental for the final device operation than the gain obtained from the reduced reflectance.
Black silicon can also be used in other technologies than solar cells. Numerous applications suggested for b-Si include drug analysis.
Black silicon (b-Si) has been a subject of great interest in various fields including photovoltaics for its ability to reduce the surface reflectance even below 1 per cent. However, many b-Si applications - especially solar cells - suffer from increased surface recombination resulting in poor spectral response. This is particularly problematic at short wavelengths.
The research has just been published in the Journal of Photovoltaics. The research is carried out by Aalto University, Finland, together with experts from Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE.
####
About Aalto University
Aalto University, Finland is a new multidisciplinary science and art community in the fields of science, economics, and art and design. The University is founded on Finnish strengths, and its goal is to develop as a unique entity to become one of the world's top universities. Aalto University's cornerstones are its strengths in education and research. At the new University, there are 20,000 basic degree and graduate students as well as a staff of 5,000 of which 350 are professors.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Päivikki Repo
Aalto University
+358 504361156
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








