Home > Press > How to treat heat like light: New approach using nanoparticle alloys allows heat to be focused or reflected just like electromagnetic waves
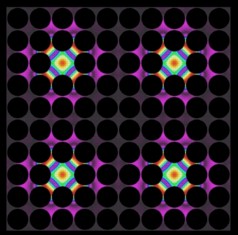 |
| Thermal lattices, shown here, are one possible application of the newly developed thermocrystals. In these structures, where precisely spaced air gaps (dark circles) control the flow of heat, thermal energy can be "pinned" in place by defects introduced into the structure (colored areas). Illustration courtesy of Martin Maldovan |
Abstract:
An MIT researcher has developed a technique that provides a new way of manipulating heat, allowing it to be controlled much as light waves can be manipulated by lenses and mirrors.
How to treat heat like light: New approach using nanoparticle alloys allows heat to be focused or reflected just like electromagnetic waves
Cambridge, MA | Posted on January 11th, 2013The approach relies on engineered materials consisting of nanostructured semiconductor alloy crystals. Heat is a vibration of matter — technically, a vibration of the atomic lattice of a material — just as sound is. Such vibrations can also be thought of as a stream of phonons — a kind of "virtual particle" that is analogous to the photons that carry light. The new approach is similar to recently developed photonic crystals that can control the passage of light, and phononic crystals that can do the same for sound.
The spacing of tiny gaps in these materials is tuned to match the wavelength of the heat phonons, explains Martin Maldovan, a research scientist in MIT's Department of Materials Science and Engineering and author of a paper on the new findings published Jan. 11 in the journal Physical Review Letters.
"It's a completely new way to manipulate heat," Maldovan says. Heat differs from sound, he explains, in the frequency of its vibrations: Sound waves consist of lower frequencies (up to the kilohertz range, or thousands of vibrations per second), while heat arises from higher frequencies (in the terahertz range, or trillions of vibrations per second).
In order to apply the techniques already developed to manipulate sound, Maldovan's first step was to reduce the frequency of the heat phonons, bringing it closer to the sound range. He describes this as "hypersonic heat."
"Phonons for sound can travel for kilometers," Maldovan says — which is why it's possible to hear noises from very far away. "But phonons of heat only travel for nanometers [billionths of a meter]. That's why you could't hear heat even with ears responding to terahertz frequencies."
Heat also spans a wide range of frequencies, he says, while sound spans a single frequency. So, to address that, Maldovan says, "the first thing we did is reduce the number of frequencies of heat, and we made them lower," bringing these frequencies down into the boundary zone between heat and sound. Making alloys of silicon that incorporate nanoparticles of germanium in a particular size range accomplished this lowering of frequency, he says.
Reducing the range of frequencies was also accomplished by making a series of thin films of the material, so that scattering of phonons would take place at the boundaries. This ends up concentrating most of the heat phonons within a relatively narrow "window" of frequencies.
Following the application of these techniques, more than 40 percent of the total heat flow is concentrated within a hypersonic range of 100 to 300 gigahertz, and most of the phonons align in a narrow beam, instead of moving in every direction.
As a result, this beam of narrow-frequency phonons can be manipulated using phononic crystals similar to those developed to control sound phonons. Because these crystals are now being used to control heat instead, Maldovan refers to them as "thermocrystals," a new category of materials.
These thermocrystals might have a wide range of applications, he suggests, including in improved thermoelectric devices, which convert differences of temperature into electricity. Such devices transmit electricity freely while strictly controlling the flow of heat — tasks that the thermocrystals could accomplish very effectively, Maldovan says.
Most conventional materials allow heat to travel in all directions, like ripples expanding outward from a pebble dropped in a pond; thermocrystals could instead produce the equivalent of those ripples only moving out in a single direction, Maldovan says. The crystals could also be used to create thermal diodes: materials in which heat can pass in one direction, but not in the reverse direction. Such a one-way heat flow could be useful in energy-efficient buildings in hot and cold climates.
Other variations of the material could be used to focus heat — much like focusing light with a lens — to concentrate it in a small area. Another intriguing possibility is thermal cloaking, Maldovan says: materials that prevent detection of heat, just as recently developed metamaterials can create "invisibility cloaks" to shield objects from detection by visible light or microwaves.
Written by David Chandler, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








