Home > Press > New technology allows scientists to capture and preserve cancer cells circulating in the bloodstream
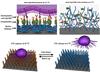 |
| A new-generation nano-platform capable of capturing circulating tumor cells and releasing them at reduced temperature. |
Abstract:
Scientists from the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute in Japan and University of California Los Angeles report a new nanoscale Velcro-like device that captures and releases tumor cells that have broken away from primary tumors and are circulating in the bloodstream.This new nanotechnology could be used for cancer diagnosis and give insight into the mechanisms of how cancer spreads throughout the body. The device provides a convenient and non-invasive alternative to biopsy, the current method for diagnosis of metastatic cancer. It could enable doctors to detect tumor cells that circulate in cancer patients' blood well before they subsequently colonize as tumors in other organs. The device also enables researchers to keep the tumor cells alive and subsequently study them.
New technology allows scientists to capture and preserve cancer cells circulating in the bloodstream
Wako, Japan | Posted on December 17th, 2012The device was developed by a team led by Hsiao-hua Yu from the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute in Japan and Hsian-Rong Tseng from the Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology at the University of California Los Angeles, in research published online today in the journal Advanced Materials.
Similar cell-capture devices have been reported but this technology is unique in that it is capable of catching the tumor cells with great efficiency and releasing them with great cell viability. Blood is passed through the device like a filter that contains a molecule capable of adhering to tumor cells like Velcro and separating them with efficiency ranging from 40% to 70%. The cancer cells are retained by tiny temperature-responsive polymer brushes inside the device. At 37 degrees Celsius, these polymer brushes stick to the tumor cells, but when cooled to 4 degrees Celsius, they release them, allowing scientists to examine the cells.
"Until now, most devices have demonstrated the ability to capture circulating tumor cells with high efficiency. However, it is equally important to release these captured cells, to preserve and study them in order to obtain insightful information about them. This is the big difference with our device." Explains Hsiao-hua Yu, who led the team that developed the technique to coat the device with polymer brushes.
Full bibliographic information
Shuang Hou, Haichao Zhao, Libo Zhao, Qinglin Shen, Kevin S. Wei, Daniel Y. Suh, Aiko Nakao, Bin Xiong, Shyh-Chyang Luo,Hsian-Rong Tseng,Hsiao-hua Yu "Capture and Stimulated Release of Circulating Tumor Cells on Polymer-Grafted Silicon Nanostructures." Advanced Materials, 2012
####
About RIKEN
RIKEN is Japan’s flagship research institute devoted to basic and applied research. Over 2500 papers by RIKEN researchers are published every year in reputable scientific and technical journals, covering topics ranging across a broad spectrum of disciplines including physics, chemistry, biology, medical science and engineering. RIKEN’s advanced research environment and strong emphasis on interdisciplinary collaboration has earned itself an unparalleled reputation for scientific excellence in Japan and around the world. Reach us on Twitter: @rikenresearch
About the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
The RIKEN Advanced Science Institute (ASI) is an interdisciplinary research institute devoted to fostering creative, curiosity-driven basic research and sowing the seeds for innovative new projects. With more than 700 full-time researchers, the ASI acts as RIKEN's research core, supporting inter-institutional and international collaboration and integrating diverse scientific fields including physics, chemistry, engineering, biology and medical science.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Juliette Savin
Global Relations Office
RIKEN
Tel: +81-(0)48-462-1225
Or
Shaun Mason
Media Relations Director
Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center
UCLA
Broad Stem Cell Research Center
UCLA
Direct line: +1 - 310-206-2805
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








