Home > Press > Researchers Develop New, Less Expensive Nanolithography Technique
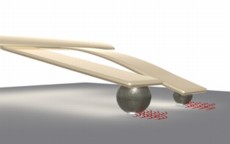 |
| This technique uses no electronic components to bring the cantilevers into contact with the substrate surface. |
Abstract:
"Parallel Dip-Pen Nanolithography using Spore- and Colloid-Terminated Cantilevers"
Authors: Marcus A. Kramer and Albena Ivanisevic, North Carolina State University
Published: Online Aug. 17 in Small
Abstract: Parallel dip-pen nanolithography is used to generate micrometer-scale patterns with protein and lipid dyes on both a glass surface and spore layer. Spore- and colloid-based tips are used to facilitate parallel patterning.
Researchers Develop New, Less Expensive Nanolithography Technique
Raleigh, NC | Posted on September 1st, 2012Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new nanolithography technique that is less expensive than other approaches and can be used to create technologies with biomedical applications.
"Among other things, this type of lithography can be used to manufacture chips for use in biological sensors that can identify target molecules, such as proteins or genetic material associated with specific medical conditions," says Dr. Albena Ivanisevic, co-author of a paper describing the research. Ivanisevic is an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and associate professor of the joint biomedical engineering program at NC State and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Nanolithography is a way of printing patterns at the nanoscale.
The new technique relies on cantilevers, which are 150-micron long silicon strips. The cantilevers can be tipped with spheres made of polymer or with naturally occurring spores. The spheres and spores are coated with ink and dried. The spheres and spores are absorbent and will soak up water when exposed to increased humidity.
As a result, when the cantilevers are exposed to humidity in a chamber, the spheres and spores absorb water - making the tips of the cantilevers heavier and dragging them down into contact with any chosen surface.
Users can manipulate the size of the spheres and spores, which allows them to control the patterns created by the cantilevers. For example, at low humidity, a large sphere will absorb more water than a small sphere, and will therefore be dragged down into contact with the substrate surface. The small sphere won't be lowered into contact with the surface until it is exposed to higher humidity and absorbs more water.
Further, the differing characteristics of sphere polymers and spores mean that they absorb different amounts of water when exposed to the same humidity - giving users even more control of the nanolithography.
"This technique is less expensive than other device-driven lithography techniques used for microfabrication because the cantilevers do not rely on electronic components to bring the cantilevers into contact with the substrate surface," Ivanisevic says. "Next steps for this work include using this approach to fabricate lithographic patterns onto tissue for use in tissue regeneration efforts."
The paper, "Parallel Dip-Pen Nanolithography using Spore- and Colloid-Terminated Cantilevers," was published online Aug. 17 in the journal Small. Lead author of the paper is Dr. Marcus A. Kramer, who did the work at NC State while completing his Ph.D. at Purdue University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
News Services
919.515.6386
Dr. Albena Ivanisevic
919.515.4683
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








