Home > Press > The Laser Beam as a “3D Painter”
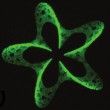 |
| A complex 3D pattern created using photografting – an Echinodermania. |
Abstract:
With laser beams, molecules can be fixed at exactly the right position in a three dimensional material. A new method developed at the Vienna University of Technology can be used to grow biological tissue or to create micro sensors.
The Laser Beam as a “3D Painter”
Germany | Posted on August 25th, 2012With laser beams, molecules can be fixed at exactly the right position in a three dimensional material. A new method developed at the Vienna University of Technology can be used to grow biological tissue or to create micro sensors.
There are many ways to create three dimensional objects on a micrometer scale. But how can the chemical properties of a material be tuned to micrometer precision? Scientists at the Vienna University of Technology have developed a method to attach molecules at exactly the right place. When biological tissue is grown, this method can allow the positioning of chemical signals, telling living cells where to attach. The new technique also holds promise for sensor technology: A tiny three dimensional "lab on a chip" could be created, in which accurately positioned molecules react with substances from the environment.
Materials Science and Chemistry
"3D-photografting" is the name of the new method. Two research teams from the Vienna University of Technology collaborated closely to develop it: Professor Jürgen Stampfl's materials science team and Professor Robert Liska's research group for macromolecular chemistry.
Both research groups have already attracted considerable attention in the past, developing new kinds of 3D-printers. However, for the applications on which the scientists are working on now, 3D-printing would not have been useful: "Putting together a material from tiny building blocks with different chemical properties would be extremely complicated", says Aleksandr Ovsianikov. "That is why we start from a three dimensional scaffold and then attach the desired molecules at exactly the right positions."
Molecules in the Hydrogel - Locked into Position by the Laser
The scientists start with a so-called hydrogel - a material made of macromolecules, arranged in a loose meshwork. Between those molecules, large pores remain, through which other molecules or even cells can migrate.
Specially selected molecules are introduced into the hydrogel meshwork, then certain points are irradiated with a laser beam. At the positions where the focused laser beam is most intense, a photochemically labile bond is broken. That way, highly reactive intermediates are created which locally attach to the hydrogel very quickly. The precision depends on the laser's lens system, at the Vienna University of Technology a resolution of 4 µm could be obtained. "Much like an artist, placing colors at certain points of the canvas, we can place molecules in the hydrogel - but in three dimensions and with high precision", says Aleksandr Ovsianikov.
Chemical Signals for Cells
This method can be used to artificially grow biological tissue. Like a climbing plant clinging to a rack, cells need some scaffold at which they attach. In a natural tissue, the extracellular matrix does the trick by using specific amino acid sequences to signal the cells, where they are supposed to grow.
In the lab, scientists are trying to use similar chemical signals. In various experiments, cell attachment could be guided on two dimensional surfaces, but in order to grow larger tissues with a specific inner structure (such as capillaries), a truly three dimensional technique is required.
Micro Sensors Detect Molecules
Depending on the application, different molecules can be used. 3D photografting is not only useful for bio-engineering but also for other fields, such as photovoltaics or sensor technology. In a very small space, molecules can be positioned which attach to specific chemical substances and allow their detection. A microscopic three-dimensional "lab on a chip" becomes possible.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library:
Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library:
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








