Home > Press > Hark! Group Demonstrates First Heralded Single Photon Source Made from Silicon
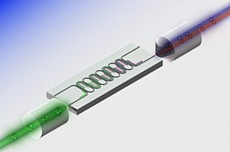 |
| Illustration of the process of photon pair generation, in which input pump photons spontaneously generate special pairs of new photons that emerge at precisely the same time, with one at a slightly lower frequency and the other a slightly higher frequency, after which heralding occurs. Credit: Srinivasan, Davanco/NIST |
Abstract:
In an important step towards more practical quantum information processing, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the University of California, San Diego; and the Politecnico di Milano in Milan, Italy, have demonstrated the first heralded single photon source made from silicon. This source complements two other recently developed silicon-based technologies—interferometers for manipulating the entanglement of photons and single photon detectors—needed to build a quantum optical circuit or a secure quantum communication system.
heralded photons
Hark! Group Demonstrates First Heralded Single Photon Source Made from Silicon
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on June 28th, 2012The line between "interesting" and practical in advanced electronics and optics often comes down to making the new device compatible with existing technology. According to NIST scientist Kartik Srinivasan, the new 0.5 mm x 0.05 mm-sized heralded photon generator meshes with existing technology in three important ways: it operates at room temperature; it produces photons compatible with existing telecommunications systems (wavelengths of about 1550 nanometers); and it's in silicon, and so can be built using standard, scalable fabrication techniques.
A "heralded" photon is one of a pair whose existence is announced by the detection of its partner—the "herald" photon. To get heralded single photons, the group built upon a technique previously demonstrated in silicon called photon pair generation.
In photon pair generation, a laser pumps photons into a material whose properties cause two incoming pump photons to spontaneously generate a new pair of frequency-shifted photons. However, while these new photons emerge at precisely the same time, it is impossible to know when that will occur.
"Detecting one of these photons, therefore, lets us know to look for its partner," says Srinivasan. "While there are a number of applications for photon pairs, heralded pairs will sometimes be needed, for example, to trigger the storage of information in future quantum-based computer memories."
According to Srinivasan, the group's silicon-based device efficiently produced pairs of single photons, and their experiment clearly demonstrated they could herald the presence of one photon by the detection of the other.
While the new device is a step forward, it is not yet practical, according to co-author Professor Shayan Mookherjea at UC San Diego, because a single source is not bright enough and a number of other required functions need to be integrated onto the chip. However, putting multiple sources along with their complementary components onto a single chip—something made possible by using silicon-based technology—could supply the performance needed for practical applications.
The work was among the three finalists and received an honorable mention in the Maiman Student Paper Competition.
####
About National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mark Esser
301-975-8735
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








