Home > Press > Nanoparticles seen as artificial atoms: Berkeley Lab researchers observations of nanorod crystal growth points way to next-generation energy devices
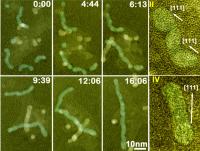 |
| These are sequential color TEM images showing the growth of Pt3Fe nanorods over time, displayed as minutes:seconds. At the far right, twisty nanoparticle chains straighten and stretch into nanorods.
Credit: Images courtesy of Haimei Zheng |
Abstract:
In the growth of crystals, do nanoparticles act as "artificial atoms" forming molecular-type building blocks that can assemble into complex structures? This is the contention of a major but controversial theory to explain nanocrystal growth. A study by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) may resolve the controversy and point the way to energy devices of the future.
Nanoparticles seen as artificial atoms: Berkeley Lab researchers observations of nanorod crystal growth points way to next-generation energy devices
Berkeley, CA | Posted on May 24th, 2012Led by Haimei Zheng, a staff scientist in Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, the researchers used a combination of transmission electron microscopy and advanced liquid cell handling techniques to carry out real-time observations of the growth of nanorods from nanoparticles of platinum and iron. Their observations support the theory of nanoparticles acting like artificial atoms during crystal growth.
"We observed that as nanoparticles become attached they initially form winding polycrystalline chains," Zheng says. "These chains eventually align and attach end-to-end to form nanowires that straighten and stretch into single crystal nanorods with length-to-thickness ratios up to 40:1. This nanocrystal growth process, whereby nanoparticle chains as well as nanoparticles serve as the fundamental building blocks for nanorods, is both smart and efficient."
Zheng is the corresponding author of a paper describing this research in the journal Science. The paper is titled "Real-Time Imaging of Pt3Fe Nanorod Growth in Solution." Co-authors are Hong-Gang Liao, Likun Cui and Stephen Whitelam.
If the near limitless potential of nanotechnology is to even be approached, scientists will need a much better understanding of how nano-sized particles can assemble into hierarchical structures of ever-increasing organization and complexity. Such understanding comes from tracking nanoparticle growth trajectories and determining the forces that guide these trajectories.
Through the use of transmission electron microscopy and liquid observation cells, scientists at Berkeley Lab and elsewhere have made significant progress in observing nanoparticle growth trajectories, including the oriented attachment of nanoparticles - the chemical phenomenon that starts the growth of nanocrystals in solution. However, these observations have typically been limited to the first few minutes of crystal growth. In their study, Zheng and her colleagues were able to extend the time of observation from minutes to hours.
"The key to studying the growth of colloidal nanocrystals with different shapes and architectures is to maintain the liquid in the viewing window long enough to allow complete reactions," Zheng says. "We dissolved molecular precursors of platinum and iron in an organic solvent and used capillary pressure to draw the growth solution into a silicon-nitride liquid cell that we sealed with epoxy. The sealing of the cell was especially important as it helped keep the liquid from turning viscous over time. Previously, we'd often see the liquids become viscous and this would prevent the nanoparticle interactions that drive crystal growth from taking place."
Zheng and her colleagues chose to study the growth of platinum iron nanorods because of the electrocatalytic material's promising potential for use in next generation energy conversion and storage devices. They were able to observe these nanoparticles assemble into nanorod crystals using powerful transmission electron microscopes at Berkeley Lab's National Center for Electron Microscopy, including TEAM 0.5 (Transmission Electron Aberration-corrected Microscope), which can produce images with half angstrom resolution - less than the diameter of a single hydrogen atom.
"From what we observed only single nanoparticles exist at the beginning of crystal growth, but, as growth proceeds, small chains of nanoparticles become dominant until, ultimately, only long chains of nanoparticles can be seen," Zheng says. "Our observations provide a link between the world of single molecules and hierarchical nanostructures, paving the way for the rational design of nanomaterials with controlled properties."
This research was supported by the DOE Office of Science.
####
About DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
awrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science, the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
510-486-5375
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Synthetic Biology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








