Home > Press > Fabrication Method Can Affect the Use of Block Copolymer Thin Films
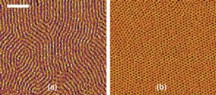 |
| The method of creating a thin film can have great effect on the material, such as the orientation of the tiny cylinders in this film proposed for use in computer memory. One method of film creation is far more effective at creating copolymer films with cylinders that stand on end (b), as they must to be usable. Scale bar represents 200 nanometers. Credit: NIST |
Abstract:
A new study by a team including scientists from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) indicates that thin polymer films can have different properties depending on the method by which they are made. The results* suggest that deeper work is necessary to explore the best way of creating these films, which are used in applications ranging from high-tech mirrors to computer memory devices.
Fabrication Method Can Affect the Use of Block Copolymer Thin Films
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on May 4th, 2012Thin films spread atop a surface have many applications in industry. Inexpensive organic solar cells might be made of such films, to name one potential use. Typically they're made by dissolving the polymer, and then spreading a small amount of the liquid out on a surface, called a substrate. The solution becomes a film as the solvent dries and the remainder solidifies. But as this happens, stresses develop within the film that can affect its structure.
Manufacturers would like to know more about how to control these stresses to ensure the film does what they want. But scientists who study film formation often use a different method of casting films than a manufacturer would. One method used in industry is "flow coating"—similar to spreading frosting across a cake. Another method is "spin casting"—placing a drop of liquid on a substrate that spins rapidly and spreads the droplet out evenly by centrifugal force. Both methods create smooth films generally, but the team decided to examine whether the two methods create different effects in finished films consisting of a self-assembling block copolymer.
"It's an important question because some proposed applications intend to take advantage of these effects," Douglas says.
The team's comparison led to results that surprised them. Although the rapid spinning of spin casting is very dynamic, suggesting it would convey more stress to the resulting film, it actually led to fewer residual stresses than flow coating did. As previous studies have shown that leftover solvent can lead to stresses in the film, the team's new theory is that because the solvent evaporates from the developing film more slowly in flow coating, this solvent discourages the film solids from arranging themselves into the equilibrium structure.
For one example, the practical benefits of this understanding could help manufacturers who propose making computer memory devices from thin films in which the solids arrange themselves as tiny cylinders in the film. Such devices would require the cylinders to stand on end, not lay down flat.
"We find we can get them to stand up much more easily with one casting method than another," Douglas says. "If we can get better results simply by varying the mode of film casting, we need to explore more deeply what happens when you make films by different methods."
* X. Zhang, J.F. Douglas and R.L. Jones. Influence of film casting method on block copolymer ordering in thin films. Soft Matter, Mar. 21, 2012. doi:10.1039/C2SM07308K.
####
About National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chad Boutin
301-975-4261
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








