Home > Press > Tiny reader makes fast, cheap DNA sequencing feasible
 |
| University of Washington
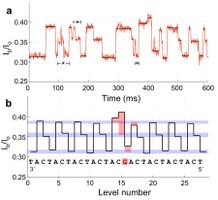
The various levels of electrical signal from the sequence of a DNA strand pulled through a nanopore reader (top) corresponds to specific DNA nucleotides, thymine, adenine, cytosine and guanine (bottom). |
Abstract:
Researchers have devised a nanoscale sensor to electronically read the sequence of a single DNA molecule, a technique that is fast and inexpensive and could make DNA sequencing widely available.
Tiny reader makes fast, cheap DNA sequencing feasible
Seattle, WA | Posted on March 26th, 2012By Vince Stricherz
News and Information
The technique could lead to affordable personalized medicine, potentially revealing predispositions for afflictions such as cancer, diabetes or addiction.
"There is a clear path to a workable, easily produced sequencing platform," said Jens Gundlach, a University of Washington physics professor who leads the research team. "We augmented a protein nanopore we developed for this purpose with a molecular motor that moves a DNA strand through the pore a nucleotide at a time."
The researchers previously reported creating the nanopore by genetically engineering a protein pore from a mycobacterium. The nanopore, from Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A, has an opening 1 billionth of a meter in size, just large enough for a single DNA strand to pass through.
To make it work as a reader, the nanopore was placed in a membrane surrounded by potassium-chloride solution, with a small voltage applied to create an ion current flowing through the nanopore. The electrical signature changes depending on the type of nucleotide traveling through the nanopore. Each type of DNA nucleotide - cytosine, guanine, adenine and thymine - produces a distinctive signature.
The researchers attached a molecular motor, taken from an enzyme associated with replication of a virus, to pull the DNA strand through the nanopore reader. The motor was first used in a similar effort by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, but they used a different pore that could not distinguish the different nucleotide types.
Gundlach is the corresponding author of a paper published online March 25 by Nature Biotechnology that reports a successful demonstration of the new technique using six different strands of DNA. The results corresponded to the already known DNA sequence of the strands, which had readable regions 42 to 53 nucleotides long.
"The motor pulls the strand through the pore at a manageable speed of tens of milliseconds per nucleotide, which is slow enough to be able to read the current signal," Gundlach said.
Gundlach said the nanopore technique also can be used to identify how DNA is modified in a given individual. Such modifications, referred to as epigenetic DNA modifications, take place as chemical reactions within cells and are underlying causes of various conditions.
"Epigenetic modifications are rather important for things like cancer," he said. Being able to provide DNA sequencing that can identify epigenetic changes "is one of the charms of the nanopore sequencing method."
Coauthors of the Nature Biotechnology paper are Elizabeth Manrao, Ian Derrington, Andrew Laszlo, Kyle Langford, Matthew Hopper and Nathaniel Gillgren of the UW, and Mikhail Pavlenok and Michael Niederweis of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
The work was funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute in a program designed to find a way to conduct individual DNA sequencing for less than $1,000. When that program began, Gundlach said, the cost of such sequencing was likely in the hundreds of thousands of dollars, but "with techniques like this it might get down to a 10-dollar or 15-minute genome project. It's moving fast."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jens Gundlach
206-616-2960
Copyright © University of Washington
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








