Home > Press > Multi-purpose photonic chip paves the way to programmable quantum processors
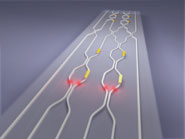 |
| Artist’s impression of the quantum photonic chip, showing the waveguide circuit (in white), and the voltage-controlled phase shifters (metal contacts on the surface). Photon pairs become entangled as they pass through the circuit. Image by University of Bristol's Centre for Quantum Photonics |
Abstract:
A multi-purpose optical chip which generates, manipulates and measures entanglement and mixture - two quantum phenomena which are essential driving forces for tomorrow's quantum computers - has been developed by researchers from the University of Bristol's Centre for Quantum Photonics. This work represents an important step forward in the race to develop a quantum computer.
Multi-purpose photonic chip paves the way to programmable quantum processors
Bristol, UK | Posted on December 12th, 2011The fundamental resource that drives a quantum computer is entanglement - the connection between two distant particles which Einstein famously called ‘spooky action at a distance'. The Bristol researchers have, for the first time, shown that this remarkable phenomenon can be generated, manipulated and measured entirely on a tiny silica chip. They have also used the same chip to measure mixture - an often unwanted effect from the environment, but a phenomenon which can now be controlled and used to characterize quantum circuits, as well as being of fundamental interest to physicists.
"In order to build a quantum computer, we not only need to be able to control complex phenomena such as entanglement and mixture, but we need to be able to do this on a chip, so that we can scalably and practically duplicate many such miniature circuits - in much the same way as the modern computers we have today," says Professor Jeremy O'Brien, Director of the Centre for Quantum Photonics. "Our device enables this and we believe it is a major step forward towards optical quantum computing."
The chip, which performs several experiments that would each ordinarily be carried out on an optical bench the size of a large dining table, is 70 mm by 3 mm. It consists of a network of tiny channels which guide, manipulate and interact single photons - particles of light. Using eight reconfigurable electrodes embedded in the circuit, photon pairs can be manipulated and entangled, producing any possible entangled state of two photons or any mixed state of one photon.
"It isn't ideal if your quantum computer can only perform a single specific task", explains Peter Shadbolt, lead author of the study, which is published in the journal Nature Photonics. "We would prefer to have a reconfigurable device which can perform a broad variety of tasks, much like our desktop PCs today - this reconfigurable ability is what we have now demonstrated. This device is approximately ten times more complex than previous experiments using this technology. It's exciting because we can perform many different experiments in a very straightforward way, using a single reconfigurable chip."
The researchers, who have been developing quantum photonic chips for the past six years, are now working on scaling up the complexity of this device, and see this technology as the building block for the quantum computers of the future.
Dr Terry Rudolph from Imperial College in London, UK, believes this work is a significant advance. He said: "Being able to generate, manipulate and measure entanglement on a chip is an awesome achievement. Not only is it a key step towards the many quantum technologies - such as optical quantum computing - which are going to revolutionize our lives, it gives us much more opportunity to explore and play with some of the very weird quantum phenomena we still struggle to wrap our minds around. They have made it so easy to dial up in seconds an experiment that used to take us months, that I'm wondering if even I can run my own experiment now!"
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © University of Bristol
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








