Home > Press > Nanotribology: Tubular probes: Short, capped single-walled carbon nanotubes may serve as ideal probing tips to study friction, lubrication and wear at the microscale
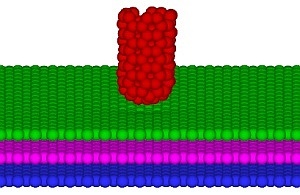 |
| Atomistic simulations show that short, capped single-walled carbon nanotubes (red) can elucidate the tribological properties of graphene surfaces Copyright : 2011 Elsevier |
Abstract:
Studying microscopic interactions at single asperities is vital for the understanding of friction and lubrication at the macroscale. Surface probe instruments with carbon nanotube tips may enable such investigations, as now demonstrated in a theoretical study led by Ping Liu and Yong-Wei Zhang at the A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing1. The researchers showed that short, single-walled, capped carbon nanotubes are able to capture the frictional characteristics of graphene with atomic resolution.
Nanotribology: Tubular probes: Short, capped single-walled carbon nanotubes may serve as ideal probing tips to study friction, lubrication and wear at the microscale
Singapore | Posted on November 29th, 2011"For an ideal probing tip, its dimension should be as small as possible, its rigidity should be as large as possible, its geometry should be well-defined, and it should be chemically inert," explains Liu. The combination of such characteristics would allow surface characterization with atomic resolution while ensuring a long lifetime and geometrical, chemical and physical stability of the tip.
Carbon nanotubes, in particular short ones, are of great interest due to their inherent strong carbon-carbon bonds, which allows them to withstand buckling and bending deformation and recover to their original shape after deformation. Capped tubes in turn offer improved chemical stability and stiffness in comparison to non-capped tubes. These considerations indicate that short, capped single-walled carbon nanotubes may be ideal imaging probe tips.
As it is not yet possible to use such tips in experimental setups, to test this hypothesis Liu and Zhang performed large-scale atomistic simulations focusing on the interaction between such nanotube probing tips and graphene (see image)—a carbon material that is ideal for surface coating lubrication. "Because of advances in the development of accurate atomic potentials and massive parallel computing algorithms, atomistic simulations not only enable us to determine the probing characteristics of such tips, but also to investigate the frictional and defect characteristics of graphene with atomic resolution," says Liu.
The simulations could capture the dependence of the friction and average normal forces on tip-to-surface distance and number of graphene layers. The researchers analyzed and interpreted the observed characteristics in terms of different types of sliding motions of the tip across the surface, as well as energy dissipation mechanisms between the tip and underlying graphene layers. They could further identify clear signatures that distinguish the motion of a tip across a point defect or the so-called Stone-Thrower-Wales defect, which is thought to be responsible for nanoscale plasticity and brittle-ductile transitions in the graphene carbon lattice. "Our simulations provide insight into nanoscale friction and may provide guidelines on how to control it," says Liu.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Institute of High Performance Computing.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Institute of High Performance Computing:
Institute of High Performance Computing:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








