Home > Press > Rice chemists cram 2 million nanorods into single cancer cell: Breakthrough in loading gold nanorods into cells could lead to new cancer treatment
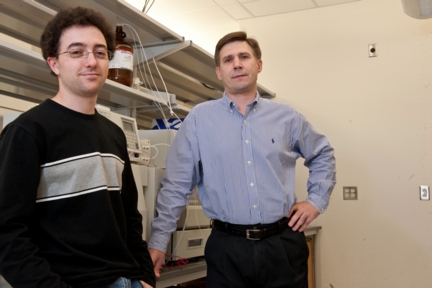 |
| Rice University's Leonid Vigderman (left) and Eugene Zubarev have found a way to load more than 2 million tiny gold particles called nanorods into a single cancer cell. CREDIT: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University |
Abstract:
Rice University chemists have found a way to load more than 2 million tiny gold particles called nanorods into a single cancer cell. The breakthrough could speed development of cancer treatments that would use nanorods like tiny heating elements to cook tumors from the inside.
Rice chemists cram 2 million nanorods into single cancer cell: Breakthrough in loading gold nanorods into cells could lead to new cancer treatment
Houston, TX | Posted on November 16th, 2011The research appears online this week in the chemical journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
"The breast cancer cells that we studied were so laden with gold nanorods that their masses increased by an average of about 13 percent," said study leader Eugene Zubarev, associate professor of chemistry at Rice. "Remarkably, the cells continued to function normally, even with all of this gold inside them."
Though the ultimate goal is to kill cancer, Zubarev said the strategy is to deliver nontoxic particles that become deadly only when they are activated by a laser.
The nanorods, which are about the size of a small virus, can harvest and convert otherwise harmless light into heat. But because each nanorod radiates miniscule heat, many are needed to kill a cell.
"Ideally, you'd like to use a low-power laser to minimize the risks to healthy tissue, and the more particles you can load inside the cell, the lower you can set the power level and irradiation time," said Zubarev, an investigator at Rice's BioScience Research Collaborative (BRC).
Unfortunately, scientists who study gold nanorods have found it difficult to load large numbers of particles into living cells. For starters, nanorods are pure gold, which means they won't dissolve in solution unless they are combined with some kind of polymer or surfactant. The most commonly used of these is cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, or CTAB, a soapy chemical often used in hair conditioner.
CTAB is a key ingredient in the production of nanorods, so scientists have often relied upon it to make nanorods soluble in water. CTAB does this job by coating the surface of the nanorods in much the same way that soap envelopes and dissolves droplets of grease in dishwater. CTAB-encased nanorods also have a positive charge on their surfaces, which encourages cells to ingest them. Unfortunately, CTAB is also toxic, which makes it problematic for biomedical applications.
In the new research, Zubarev, Rice graduate student Leonid Vigderman and former graduate student Pramit Manna, now at Applied Materials Inc., describe a method to completely replace CTAB with a closely related molecule called MTAB that has two additional atoms attached at one end.
The additional atoms -- one sulfur and one hydrogen -- allow MTAB to form a permanent chemical bond with gold nanorods. In contrast, CTAB binds more weakly to nanorods and has a tendency to leak into surrounding media from time to time, which is believed to be the underlying cause of CTAB-encased nanorod toxicity.
It took Zubarev, Vigderman and Manna several years to identify the optimal strategy to synthesize MTAB and substitute it for CTAB on the surface of the nanorods. In addition, they developed a purification process that can completely remove all traces of CTAB from a solution of nanorods.
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation.
Rice's BRC is an innovative space where scientists and educators from Rice and other institutions in the Texas Medical Center work together to perform leading research that benefits human medicine and health.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is known for its "unconventional wisdom." With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is less than 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 4 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to www.rice.edu/nationalmedia/Rice.pdf.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The report in Angewandte Chemie is available at:
The report in Angewandte Chemie is available at:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








